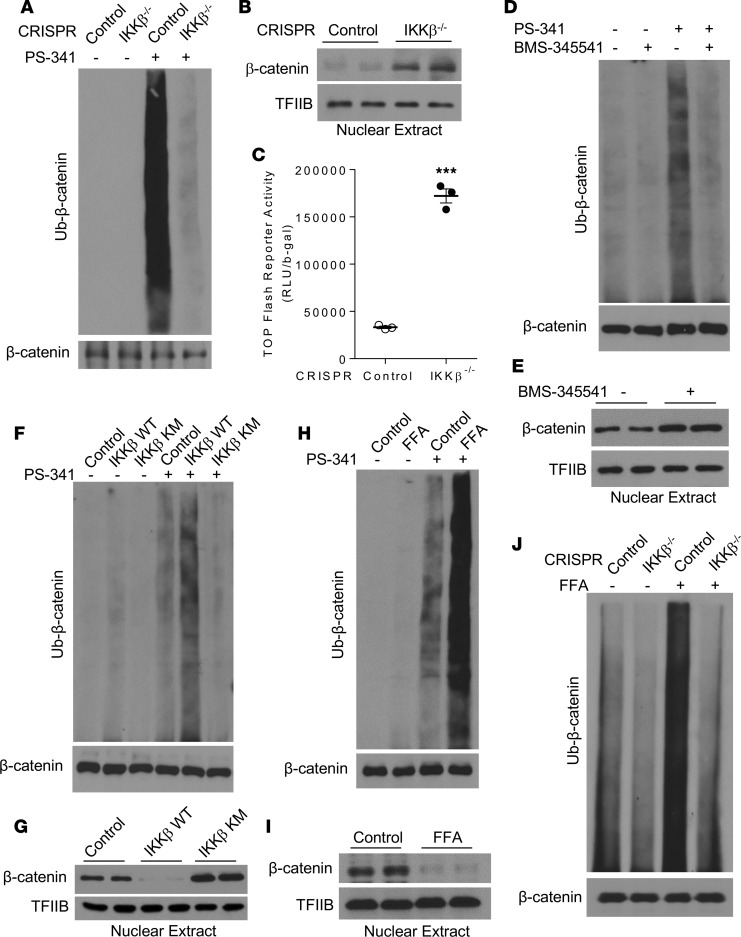
Figure 6. IKKβ regulates β-catenin ubiquitination in MSCs.
(A) Control or IKKβ-deficient C3H/10T1/2 cells were treated with vehicle or 100 nM PS-341. β-Catenin proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti–β-catenin antibodies and then probed with anti-ubiquitin antibodies. The whole cell lysates were probed with anti–β-catenin antibodies as an internal control. (B and C) Immunoblotting for nuclear β-catenin proteins (B) and β-catenin reporter activity (C) in control or IKKβ-deficient C3H/10T1/2 cells. (D and E) Immunoblotting for ubiquitinated β-catenin proteins (D) and nuclear β-catenin proteins (E) in control or BMS-345541–treated C3H/10T1/2 cells. (F and G) Immunoblotting for ubiquitinated β-catenin proteins (F) and nuclear β-catenin proteins (G) in C3H/10T1/2 cells infected with control, IKKβ WT, or IKK KM virus. (H and I) Immunoblotting for ubiquitinated β-catenin levels (H) and nuclear β-catenin proteins (I) in control or FFA-treated C3H/10T1/2 cells. (J) Immunoblotting for ubiquitinated β-catenin proteins in control or IKKβ-deficient C3H/10T1/2 cells treated with vehicle or FFAs. Error bars represent ± SEM. Significance was determined by Student’s t test (C). ***P < 0.001.