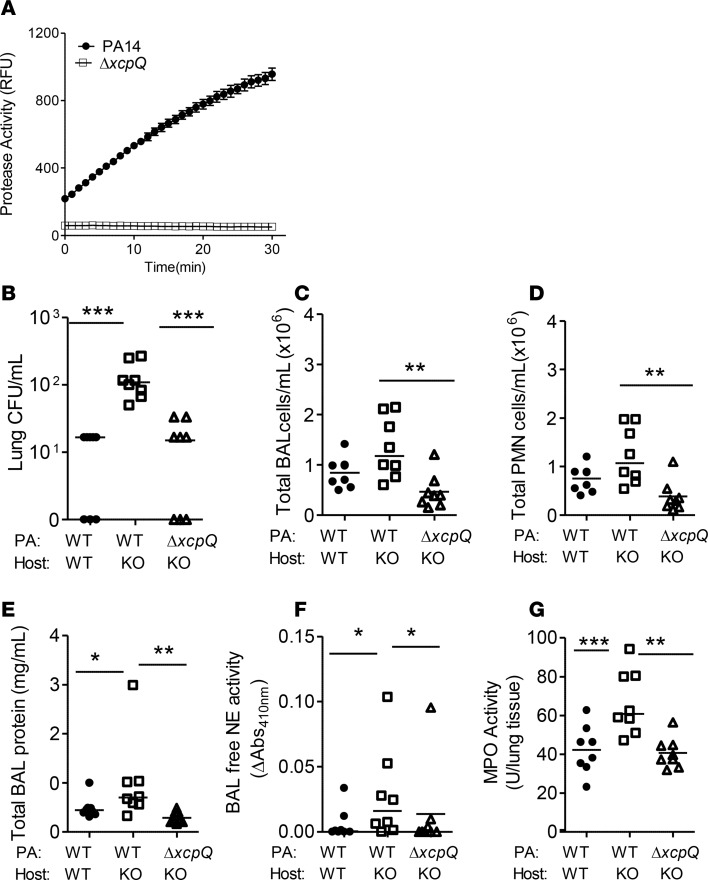
Figure 8. The ΔxcpQ mutant induces less bacterial burden, airspace neutrophil recruitment, and inflammation in Thbs1–/– mice when compared with Pseudomonas aeruginosa parent strain.
WT and Thbs1–/– (KO) mice were inoculated with P. aeruginosa (PA) parent strain PA14 or ΔxcpQ mutant strain and outcome measurements obtained 20 hours after infection (PA inoculum, 2.2 × 106 CFU; ΔxcpQ mutant inoculum, 2.5 × 106 CFU). (A) Total protease activity of cell-free supernatant (SN) from the PA14 parent strain and ΔxcpQ mutant was measured by the cleavage of fluorogenic casein substrate in relative fluorescence units (RFU) over time. (B) Lung CFU/ml, (C) total bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cell counts/ml, (D) total BAL PMN counts/ml, (E) total BAL protein concentration, (F) BAL free neutrophil elastase (NE) activity, and (G) lung tissue myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity were measured in WT and KO mice. Each data point represents an individual mouse, n = 8 mice/group. Lines indicate the median. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons.