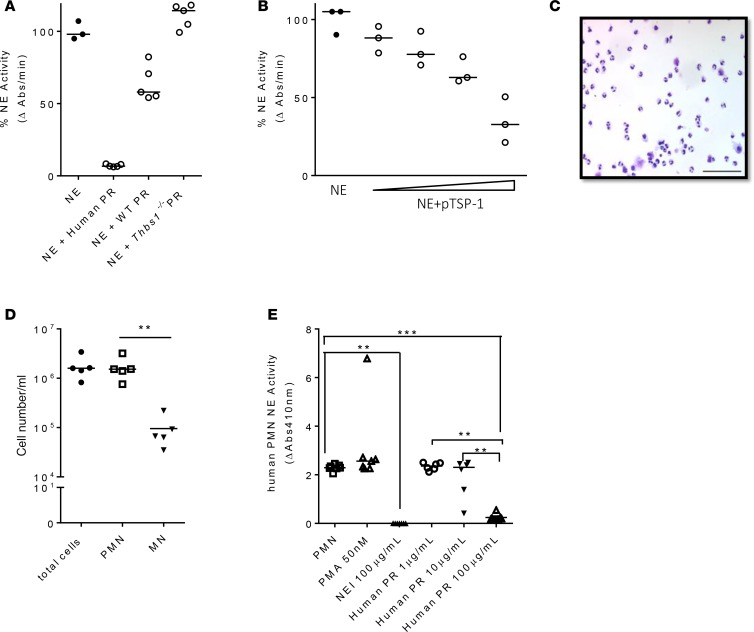
Figure 9. Platelet releasates enriched in TSP-1 dose-dependently inhibit NE activity from neutrophils isolated from tracheal secretions of mechanically ventilated ICU patients.
(A) Neutrophil elastase (NE) was incubated with human platelet releasates (PRs), WT mouse PRs, or Thbs1–/– mouse PRs for 24 hours and NE activity measured as the rate of enzymatic hydrolysis of NE substrate N-methoxysuccinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Val p-nitroanilide reflected by the increase in absorbance (Abs) at 410 nm over time. Data points indicate combined data from 2 independent studies using PRs pooled from 6–8 mice/group. Lines indicate the median. (B) Human NE was incubated with human TSP-1 at different concentrations (38.8, 77.6, 194, and 388 nM) for 10 hours and NE activity measured as the rate of enzymatic hydrolysis of NE substrate N-methoxysuccinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Val p-nitroanilide reflected by the increase in Abs at 410 nm over time. Data points indicate technical replicates from 1 experiment. Lines indicate the median. (C) Leukocytes were collected from human airway secretions, and cytospin shows predominance of neutrophils. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) Cell count and differential of isolated leukocytes. PMN, polymorphonuclear cells; MN, mononuclear cells. Each data point was obtained from individual patient tracheal samples (N = 5). (E) Isolated human airway neutrophils were incubated with PMA (50 nM), NE inhibitor (100 μg/ml, NEI), or human PR (1, 10, and 100 μg/ml). Each data point was obtained from individual patient tracheal samples (N = 7). Lines indicate the median. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.