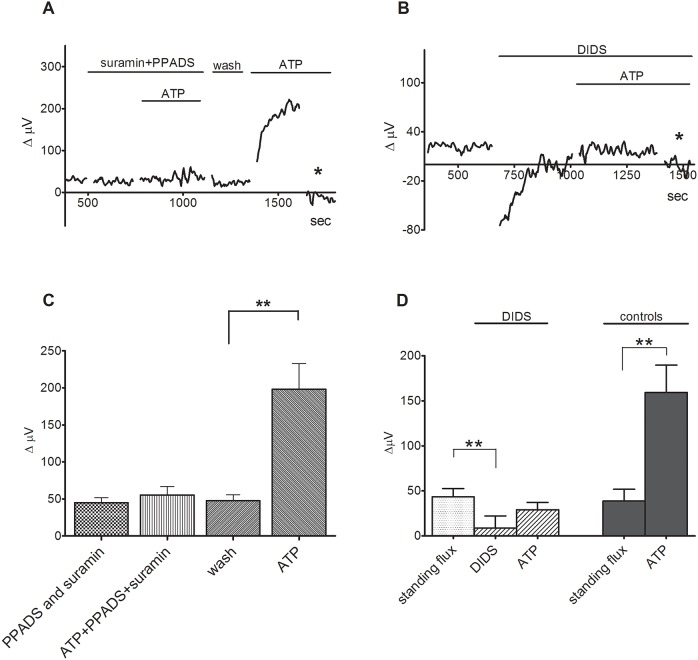
Fig 2. Inhibition by suramin, PPADS and DIDS significantly reduces the ATP-induced increase in extracellular H+ flux from isolated Müller cells.
(A) A representative trace from a single Müller cell shows a significant increase in H+ flux in response to 10 μM ATP that is significantly reduced by the ATP receptor blockers 200 μM PPADS and 200 μM suramin; asterisk indicates a background control reading. (B) 300 μM DIDS, which inhibits anion transport, significantly reduces the increase in H+ flux in response to 10 μM ATP. (C) Mean responses to 10 μM ATP with or without suramin and PPADS in the bath; N = 7, error bars represent SEMs. (D) Mean responses to 10 μM ATP in the presence of 300 μM DIDS (N = 6) and in the absence of DIDS, N = 5 (controls).