Fig 1. Sepsis induces a sustained increase of IL-10+ B cells.
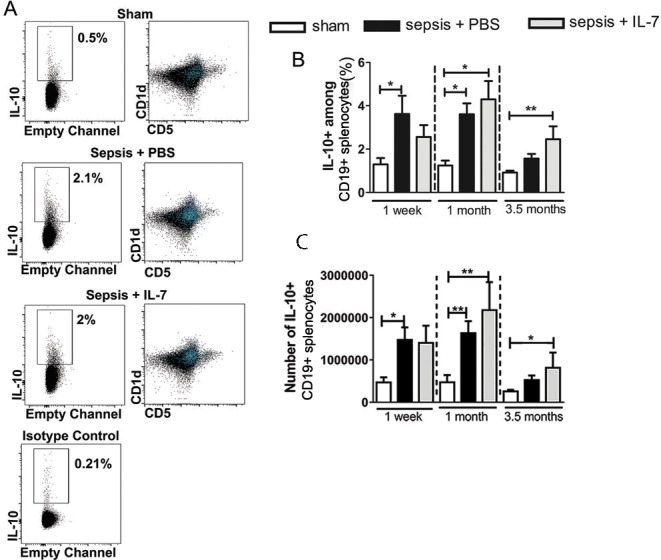
Mice were injected with PBS i.p. (Sham) or subjected to sepsis induction. IL-7 (Sepsis + IL-7) or PBS (Sepsis + PBS) was injected daily for 5 days from day 5–9 post sepsis induction. IL-10+ and CD1dhi B cells from the spleen were analysed 1 week, 1 month and 3.5 months after sepsis induction. (A) Representative flow cytometry images from analyses 1 week after sepsis induction showing IL-10+ cells among CD19+ B cells (left panel) and distribution of IL-10+ cells (blue) with respect to CD1d and CD5 markers (right panel). (B) Frequency of IL-10+ cells among CD19+ B cells. (C) Number of IL-10+ CD19+ cells in the spleen. n (number of mice per group) = 6–10 (1 week), 9–16 (1 month), 7–16 (3.5 months). *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01 (ANOVA). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Data are representative of three experiments.
