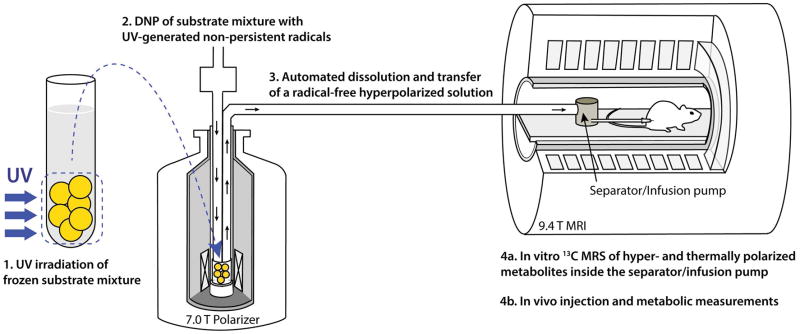
Figure 1.
Illustration of the in vivo and in vitro experimental method based on UV-irradiated 13C-labeled metabolic substrate mixtures: (1) a frozen mixture of 13C-labeled substrates, in this case [1-13C]butyric and [1-13C]pyruvic acids, is irradiated with UV light at 77 K; (2) the mixture is loaded into a DNP polarizer and 13C nuclei are dynamically polarized for 1–2 h; (3) using an automated process, the sample is quickly dissolved in superheated buffer solution and automatically transferred from the polarizer into a separator/injection pump located inside the bore of an MRI magnet; (4a & 4b) in vitro 13C MRS measurements are performed while the hyperpolarized 13C-substrate mixture is inside the separator/injection pump and/or the mixture is injected into the rat via a femoral vein catheter and in vivo hyperpolarized 13C MRS measurements are launched.