Figure 1.
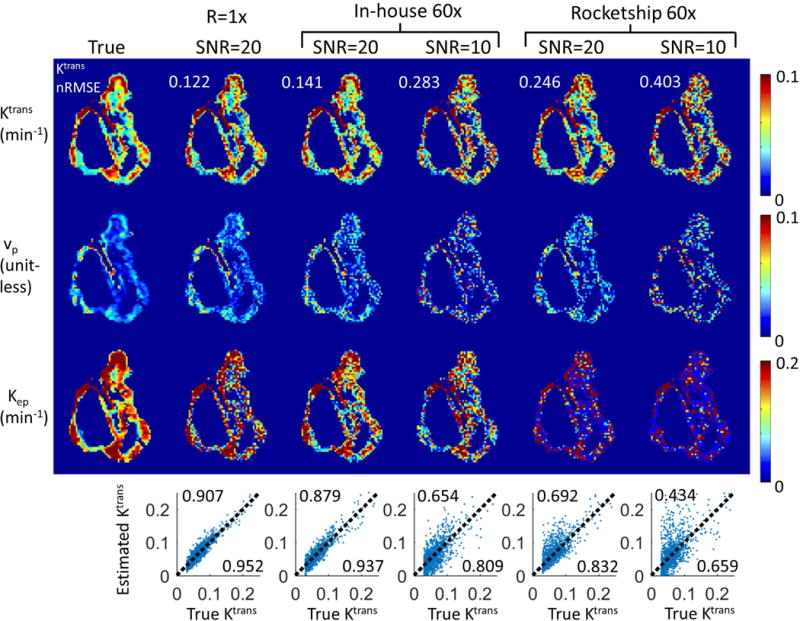
The proposed method is compatible with third-party TK solvers. Shown are results from an anatomically-realistic brain-tumor DCE-MRI digital reference object using an in-house solver and the Rocketship solver, both using the model consistency constraint method. R=60x were tested at white matter SNR level of 20 and 10. Tumor ROI Ktrans nRMSE (normalized to 90%ile value) were shown on the upper left corner of respective Ktrans maps. Correlation plots are shown at the bottom of each respective result, where the upper left corner shows the R2 value, and lower right corner shows the correlation coefficient. Both methods were able to restore Ktrans maps with less than 50% nRMSE, while the Rocketship solver yielded Ktrans maps with higher errors, especially at SNR=10. Kep and vp maps are more sensitive to noise, especially when using the Rocketship solver.
