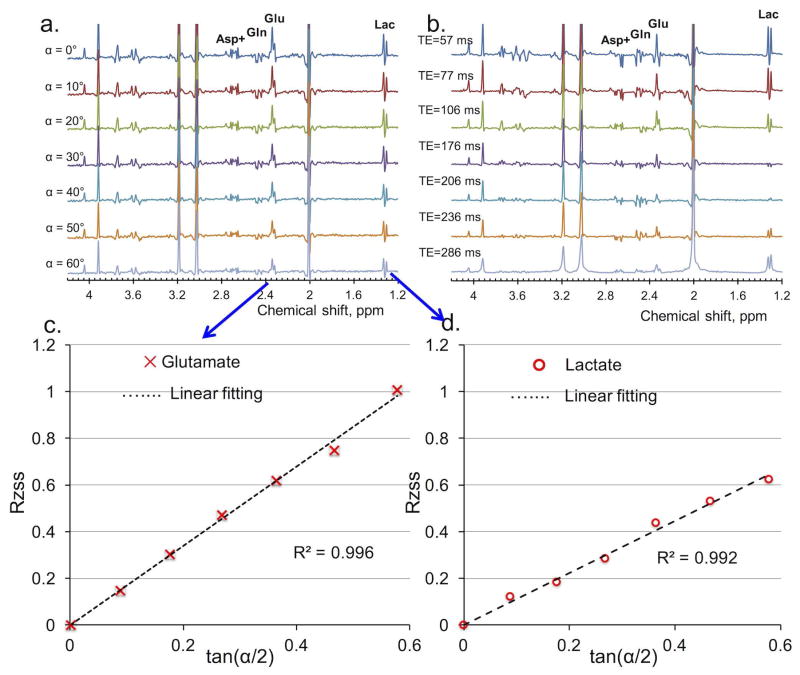
Figure 4.
Comparison of phantom results of J-coupled metabolites, such as aspartate (Asp+ (with contribution from N-acetylaspartate (NAA) aspartyl moiety), glutamine (Gln), glutamate (Glu), and lactate (Lac), between Multiple flip Angle pulse driven Ratio of longitudinal Steady States (MARZSS) and multi-echo time (TE) PRESS techniques. (a) Signal variation with flip angle in phantom measurements acquired by the proposed MARZSS. No discernable sensitivity to J-coupling of MARZSS technique was observed. Flip angles were varied from 0° to 60° with 10° increments (top to bottom). (b) Signal variation with TE in phantom measurements acquired by conventional multi-TE PRESS. High sensitivity to J-coupling of conventional multi-TE PRESS was observed. Echo times were 57, 77, 106, 176, 206, 236, 286 ms (top to bottom). (c) Linear fitting as black dotted line for Glu data points from the proposed MARZSS technique. Glu data were extracted with the LCModel from spectra shown in Fig. 4a. (d) Linear fitting as black dotted line for Lac data points from the proposed MARZSS technique. Lac data were extracted from spectra shown in Fig. 4a.