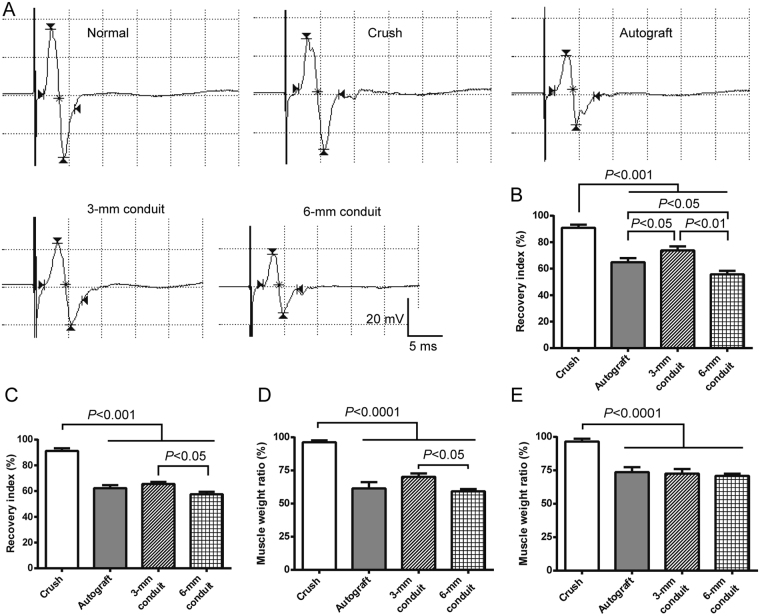
Figure 4.
Tubulation repair of the sciatic nerve gap exhibited comparable muscle re-innervation to nerve autografting 6 months post-injury. (A) Representative traces of compound muscle action potentials (CMAP) recorded in tibialis cranialis when stimulating the proximal sciatic nerve. The insert shows the scale bar for all traces. (B,C) Bar charts showing recovery index of CMAP amplitude in tibialis cranialis and gastrocnemius muscles, respectively. Recovery index was calculated as a ratio of peak CMAP amplitude on the injured side over that on the contralateral normal side. The 3-mm conduit group showed significantly improved recovery index compared to nerve autograft group. (D,E) Wet weight ratio of tibialis cranialis and gastrocnemius muscles, respectively. Data are expressed as mean±SEM (n = 10 rats each).