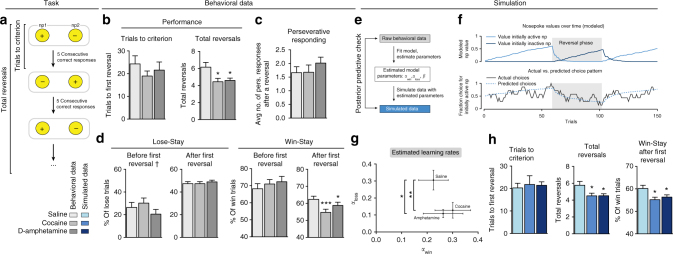
Fig. 1.
Treatment with cocaine or D-amphetamine impairs reversal learning. a Task design. b Systemic cocaine (10 mg/kg) or D-amphetamine (0.25 mg/kg) treatment did not alter the number of trials required to reach first reversal (one-way RM ANOVA, p = 0.55), but decreased the total number of reversals accomplished (ANOVA, p = 0.0037; post-hoc test versus saline, p = 0.0102 cocaine, p = 0.0197 D-amphetamine). c Treatment with cocaine or D-amphetamine did not alter perseverative behavior after a reversal (p = 0.46). d Lose-stay behavior was unaffected after cocaine or D-amphetamine treatment, both before (p = 0.21†) and after (p = 0.77) the first reversal. Cocaine and D-amphetamine decreased win-stay behavior after (ANOVA, p = 0.0007; post-hoc test versus saline, p = 0.0009 for cocaine, p = 0.0336, D-amphetamine), but not before the first reversal (p = 0.67). Repeated measures from n = 25 animals. †Six animals had no losses before the first reversal, so the ANOVA was performed on data of n = 19 animals; graph shows n = 25. e We used a modified Rescorla–Wagner model to describe the behavior of the rats during reversal learning. f Example session. (Top) Simulated values of the nose pokes, given the rat’s optimal model parameters and observed choices. (Bottom) Modeled choice probabilities, converted from the simulated nose poke values using a softmax (unsmoothed), and the rat’s actual choice pattern (smoothed over 7 trials). g Best-fit learning parameters. Treatment with cocaine and D-amphetamine decreased αloss, without affecting the other model coefficients (Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, *p = 0.032, **p = 0.0046, see Supplementary Table 2). h Simulating data with the model parameters extracted in g replicated the drug-induced effects of the behavioral data (n = 25 simulated rats; ANOVA trials to criterion, p = 0.86; total reversals, p = 0.0114, post-hoc test, p = 0.0411 for cocaine, and p = 0.0215 for D-amphetamine; ANOVA win-stay, p = 0.0090, post-hoc test, p = 0.0181 for cocaine and p = 0.0462 for D-amphetamine. ANOVA on all other measures, p > 0.1). Data shown as mean ± standard error of the mean; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001