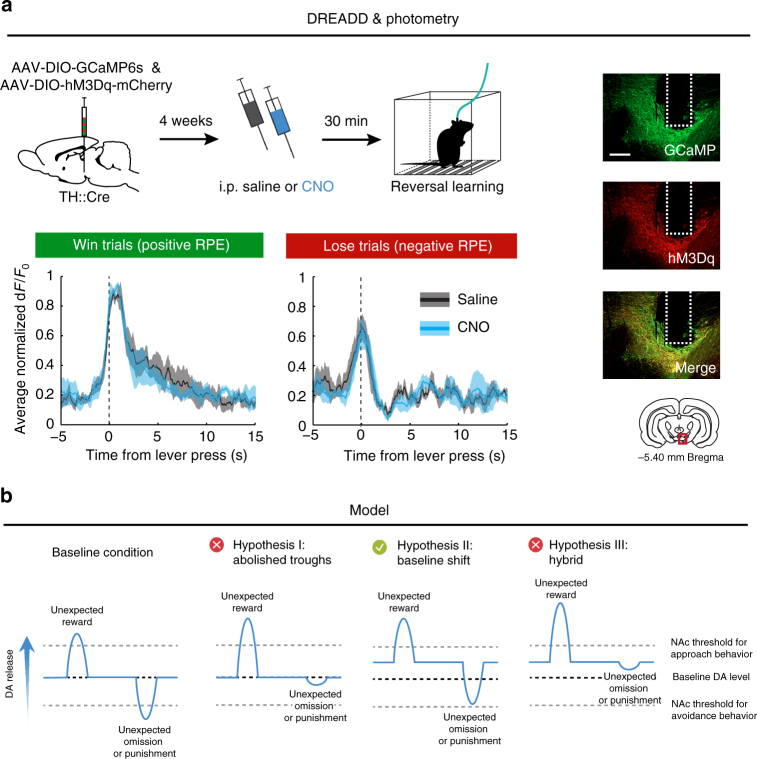
Fig. 7.
Reward prediction error processing after mesoaccumbens stimulation. a Animals were co-injected with GCaMP6s and Gq-DREADD and tested for reversal learning after injection of saline or CNO. VTA neurons responded in a comparable way during reversal learning after saline and CNO treatment (repeated measures in n = 4 animals; ANOVA, CNO×time interaction effect, win trials, p = 0.39; lose trials, p = 0.38). See Supplementary Fig. 9a for individual animals. Scale bar, 1 mm. Data are shown as mean (solid line) ± standard error of the mean (shading). b Proposed mechanisms: (I) hyperactivity of NAc-projecting VTA DA neurons leads to impaired coding of negative reward prediction error troughs, (II) hyperactivity shifts baseline NAc DA levels, thereby preventing the exceedance of a negative reward prediction error threshold in the NAc and impairing the ability to learn from negative feedback, or (III) a combination of I and II