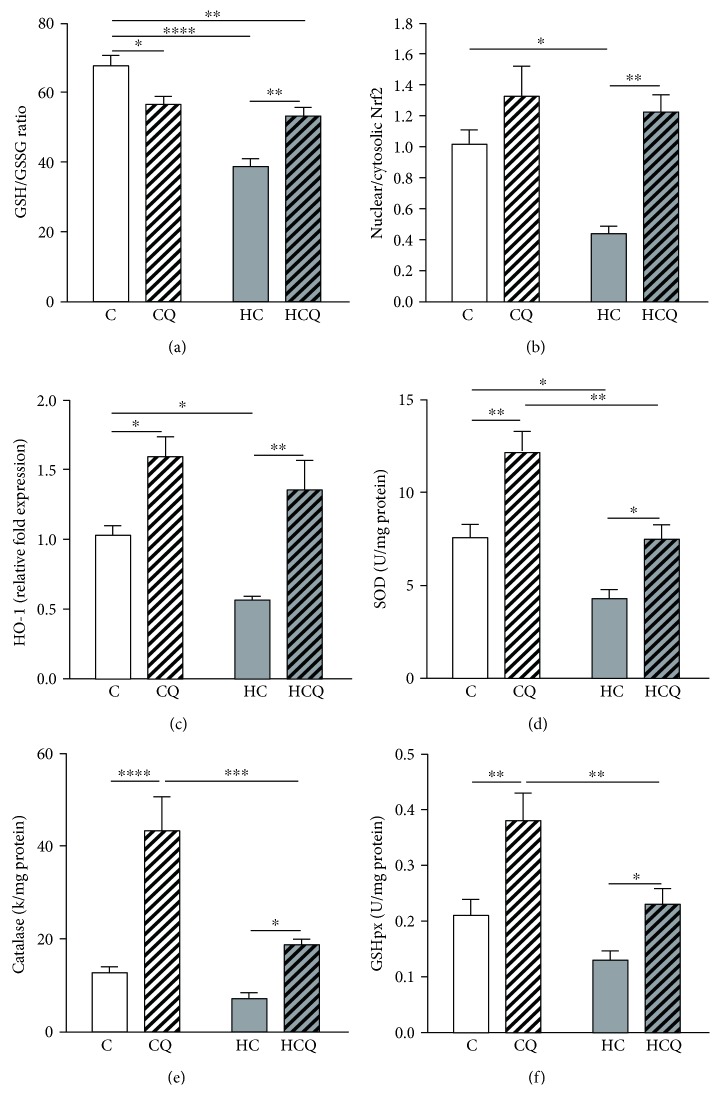
Figure 6.
Quercetin protects against the decrease in cardiac antioxidant defenses induced by high-cholesterol diet. Antioxidant defenses (a) GSH/GSSG ratio, (b) nuclear translocation of Nrf2, (c) HO-1 expression, and activities of (d) SOD, (e) catalase, and (f) glutathione peroxidase in the heart from rats fed for 4 weeks with control diet (C), control diet containing 0.5% quercetin diet (CQ), high-cholesterol diet (HC), and high-cholesterol diet containing 0.5% quercetin (HCQ). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. N = 6–8 rats/group. Two-way ANOVA test and Bonferroni posttest. Statistical differences: ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01, ∗∗∗ p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗ p < 0.0001.