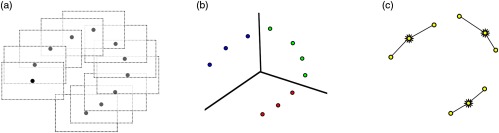
Fig. 5.
(a) The estimated cameras and plane produce drift-free estimates of the projected images in the mosaic space. We project the image corners (dotted contour) and compute the centroids (black dots). (b) The centroids have been clustered using -means. (c) A consecutive subset of centroids has been randomly selected from each cluster. These centroids correspond to fixed camera poses as well as visual measurements, which are then used to leverage the visual pairwise relations in different areas of the space.