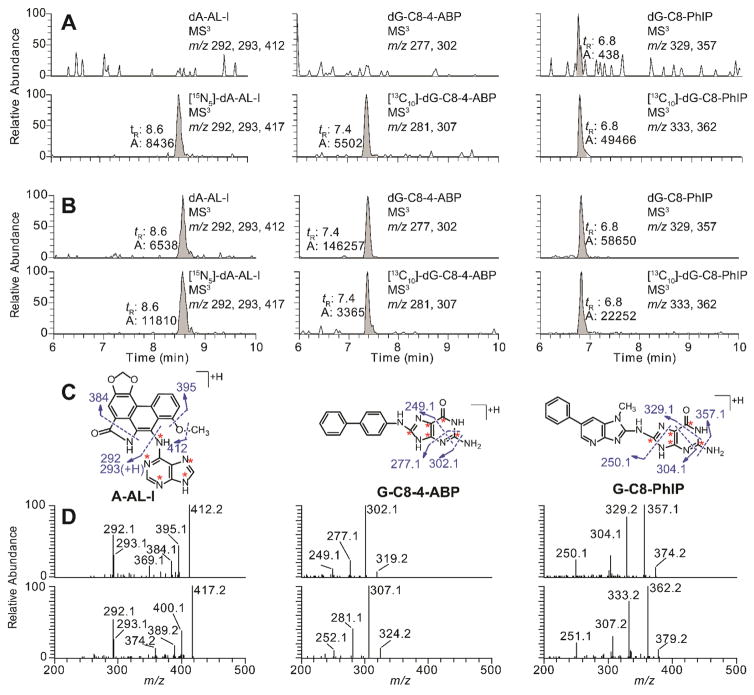
Figure 2.
EICs at the MS3 scan stage of rodent FFPE tissues samples targeting dA-AL-I, dG-C8-4-ABP, and dG-C8-PhIP. DNA samples were isolated from FFPE liver tissues of rodents employing the rapid throughput DNA isolation method. (A) EICs of negative control samples of calf thymus DNA spiked with isotope labeled internal standards; [15N5]-dA-AL-I and [13C10]-dG-C8-PhIP at a level of 5 adducts per 108 nucleotides, [13C10]-dG-C8-4-ABP at a level of 10 adducts per 108 nucleotides. (B) Representative EICs of FFPE liver samples from rodents dosed with AA-I, 4-ABP, and PhIP, respectively; (C) The structures of aglycone adducts of dA-AL-I, dG-C8-4-ABP, and dG-C8-PhIP, and proposed mechanism of fragmentation are present. The isotopically labeled 15N and 13C atoms of the internal standards are marked with red asterisks. (D) The product ion spectra of isotope labeled and unlabeled adduct of dA-AL-I, dG-C8-4-ABP, and dG-C8-PhIP.