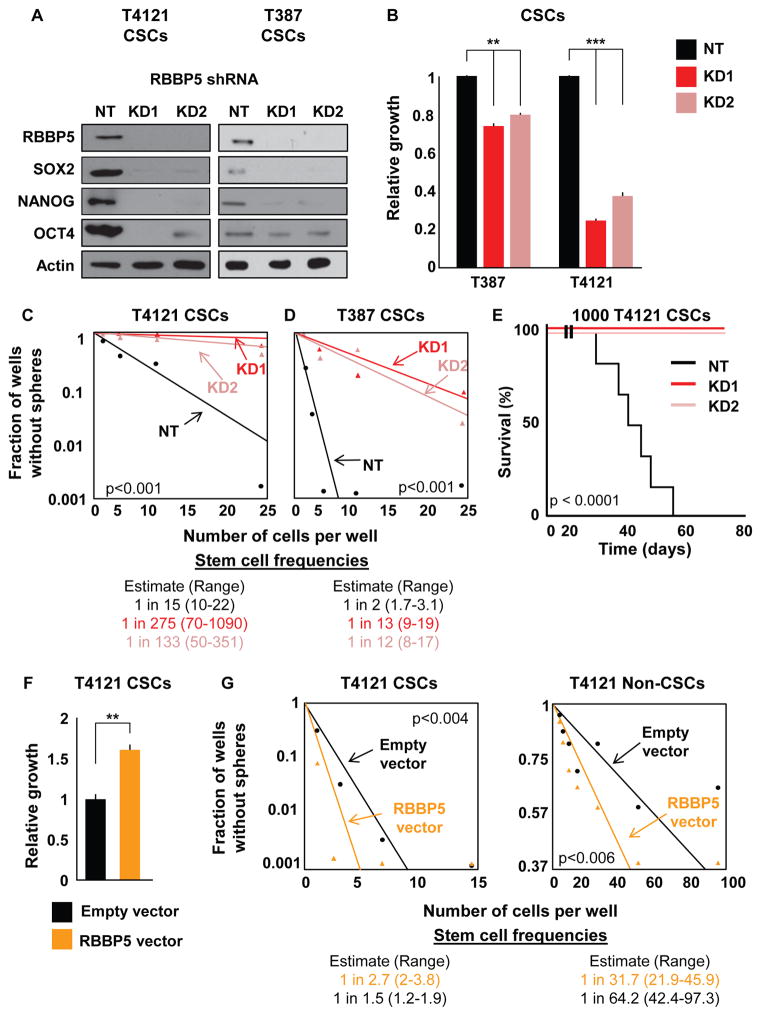
Figure 5. Targeting RBBP5 Mimics TLR4 Overexpression in CSCs.
(A) Validation of two shRNA constructs targeting RBBP5 at the protein level compared with non-targeting vector (NT). Western blots were also stained for the pluripotency factors SOX2, NANOG, and OCT4. CSCs were infected with lentivirus containing one of two different RBBP5 shRNA constructs, selected for stable expression, and assayed within five passages for all experiments. Actin was used as a loading control.
(B) The proliferation of CSCs stably expressing RBBP5 shRNA was measured and compared with an NT vector. The growth of the cells over 7 days as determined by CellTiter Glo was normalized to the growth of NT cells.
(C and D) Limiting dilution analysis of the effect of RBBP5 knockdown on two different specimens. Cells were plated in a limiting dilution manner, and the number of wells containing spheres was counted after 10 days to generate stem cell frequencies using the online algorithm detailed in the STAR Methods.
(E) Mice (n = 7 for KD, n = 6 for NT) were intracranially injected with 1000 T4121 NT or RBBP5-knockdown CSCs, and the time until endpoint was recorded. Kaplan-Meier survival plots are shown, and the log rank p value for significance between groups is shown next to the survival curve.
(F) Proliferation was analyzed after RBBP5 overexpression over 7 days in CSCs. Growth was assessed using CellTiter Glo and normalized to that of cells containing an empty vector. Cells were infected with lentivirus, selected for stable expression, and used within five passages for all experiments.
(G) Limiting dilution analyses of both CSCs and non-CSCs overexpressing RBBP5 compared with a control vector. Cells were plated in a limiting dilution manner, and the number of wells containing spheres was counted after 10 days to generate stem cell frequencies using the online algorithm detailed in the STAR Methods.
All in vitro experiments were performed at least three times. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 as assayed by one-way ANOVA. See also Figure S4.