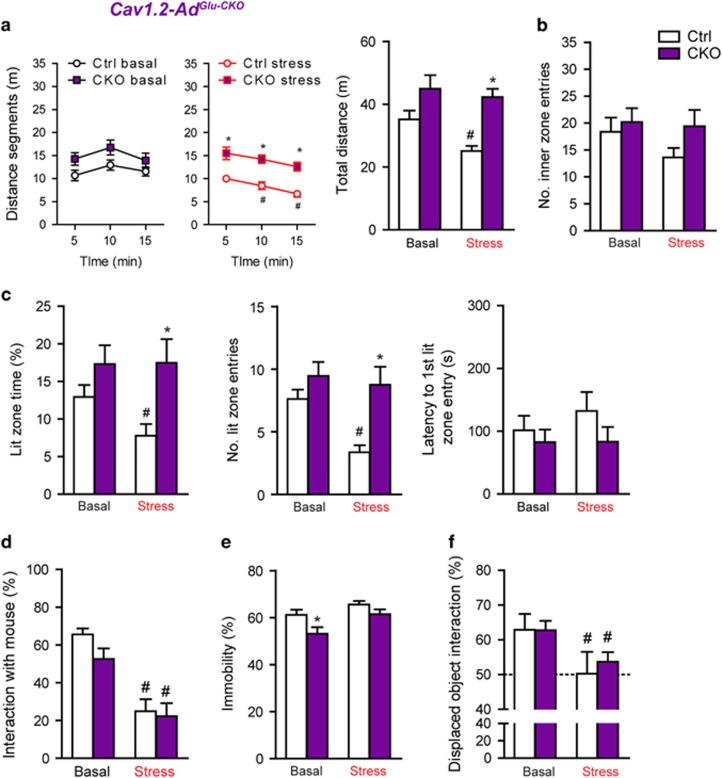
Figure 4.
Deletion of Cacna1c from forebrain glutamatergic neurons during adulthood promotes resilience to chronic social defeat stress (CSDS). (a) Locomotion (distance segments: time × stress, F2,45=10.7, P<0.0001/total distance: genotype, F1,45=19.6, P<0.0001; stress, F1,45=4.3, P=0.04) and (b) number of inner zone entries in the open field (OF). (c) Dark/light box test (Lit zone time: genotype, F1,45=9.3, P=0.004/Lit zone entries: stress, F1,45=5.8, P=0.02; genotype, F1,45=12.3, P<0.001). (d) Sociability test (stress, F1,45=52.52, P<0.0001) and (e) forced swim test (FST; genotype, F1,45=7.5, P=0.009; stress, F1,45=8.3, P=0.006). (f) Spatial object recognition test (stress, F1,42=7.1, P=0.01). Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)+Bonferroni post hoc test and repeated measures (RM)-ANOVA+Bonferroni post hoc test; *significantly different from the control (Ctrl) group of the same condition, #significantly different from the basal condition of the same genotype. OF, dark/light box test, sociability and FST (n=13 Ctrl basal, 12 Ctrl stress, 12 conditional knockout (CKO) basal, 12 Het stress). Spatial object recognition test (n=12 Ctrl basal, 10 Ctrl stress, 12 CKO basal, 12 CKO stress). Data are means±s.e.m.