Fig. 2.
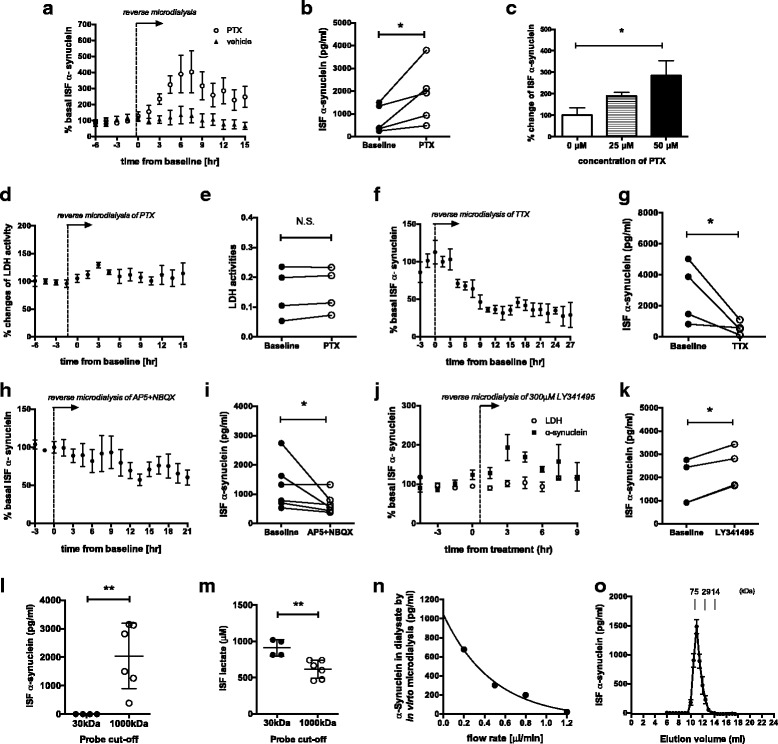
ISF α-synuclein is present as high molecular weight species and its steady-state levels are dynamically regulated by neuronal activity. a Picrotoxin (PTX, 50 μM) increased ISF α-synuclein compared to vehicle treatment. N = 4–5. b ISF α-synuclein concentrations were increased by 50 μM PTX from baseline. N = 5. c The mean ISF α-synuclein levels after 25 μM or 50 μM PTX or vehicle (0 μM) infusion were elevated dose dependently N = 4–7. d % ISF LDH activities did not alter by 50 μM PTX. N = 4. e ISF LDH activities did not change by 50 μM PTX from baseline. N = 4. f Tetrodotoxin (5 μM, TTX) decreased ISF α-synuclein N = 4. g ISF α-synuclein concentrations were decreased by TTX from baseline. N = 4. h 50 μM AP5 and 10 μM NBQX decreased ISF α-synuclein. N = 6. i ISF α-synuclein concentrations were decreased by AP5 and NBQX from baseline. N = 6. j 300 μM LY341495 increased ISF α-synuclein without changing LDH activities N = 4. k ISF α-synuclein concentrations were increased by LY341495 from baseline. N = 4. The effect of drug treatment was assessed between baseline α-synuclein levels and mean α-synuclein levels in the entire treatment period. l Absolute concentration of ISF α-synuclein collected at 1.0 μl/min through either 30 kDa membranes or 1000 kDa membranes. N = 4–6. m Absolute concentration of ISF lactate collected at 1.0 μl/min through either 30 kDa membranes or 1000 kDa membranes. N = 4–6. n α-Synuclein concentrations in dialysate collected at the different flow rate by in vitro microdialysis with 30 kDa membranes. o ISF samples obtained from wild-type mice through 1000 kDa membranes were separated by a size exclusion chromatography using a Superdex75 column. α-Synuclein levels in eluted fractions were quantified by α-synuclein ELISA (N = 4). Mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, using one-way ANOVA (c) or using ratio paired t test (b, e, g, i, k) or unpaired t test (l, m)
