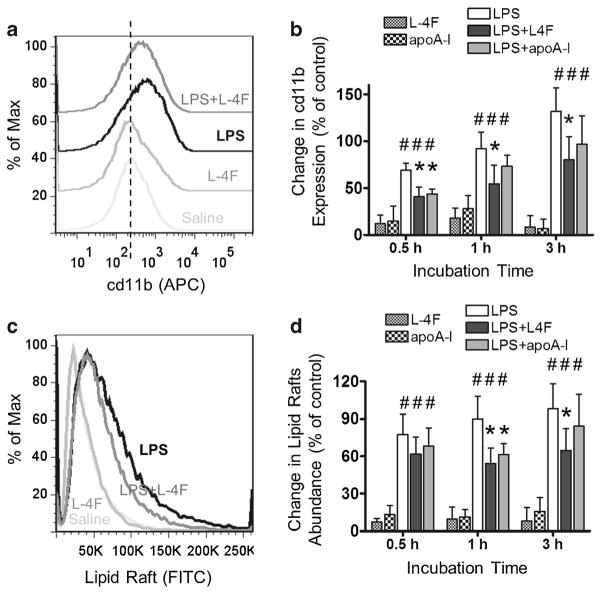
Fig. 3.
L-4F and apoA-I inhibit LPS-mediated increase in CD11b expression and lipid raft abundance in isolated human neutrophils. Isolated human neutrophils were incubated in donor plasma with saline, L-4F or apoA-I (40 μg/ml), LPS (1 μg/ml), and LPS plus L-4F or apoA-I for 30 min (n=5), 1 h (n=4), and 3 h (n=4). Following incubation, neutrophils were stained with anti-human CD11b (activation epitope) allophycocyanin (APC) and with cholera toxin B subunit FITC. Changes in CD11b expression and lipid raft abundance were measured by flow cytometry. A A representative histogram of relative changes of surface expression of CD11b for different treatments following 1 h incubation. Vertical dashed line represents median CD11b expression in control. B Statistical data presented as percent relative changes of surface expression of CD11b (mean fluorescent intensity, MFI) relative to the saline control. C A representative histogram of relative changes of lipid rafts abundance. D Statistical data presented as percent changes in lipid raft abundance (MFI) relative to the saline control. *P<0.05 vs. saline-treated LPS, #P<0.05 vs. control groups.