Extended Data Figure 4. RNA-Seq, qRT-PCR data analyses and functional classification.
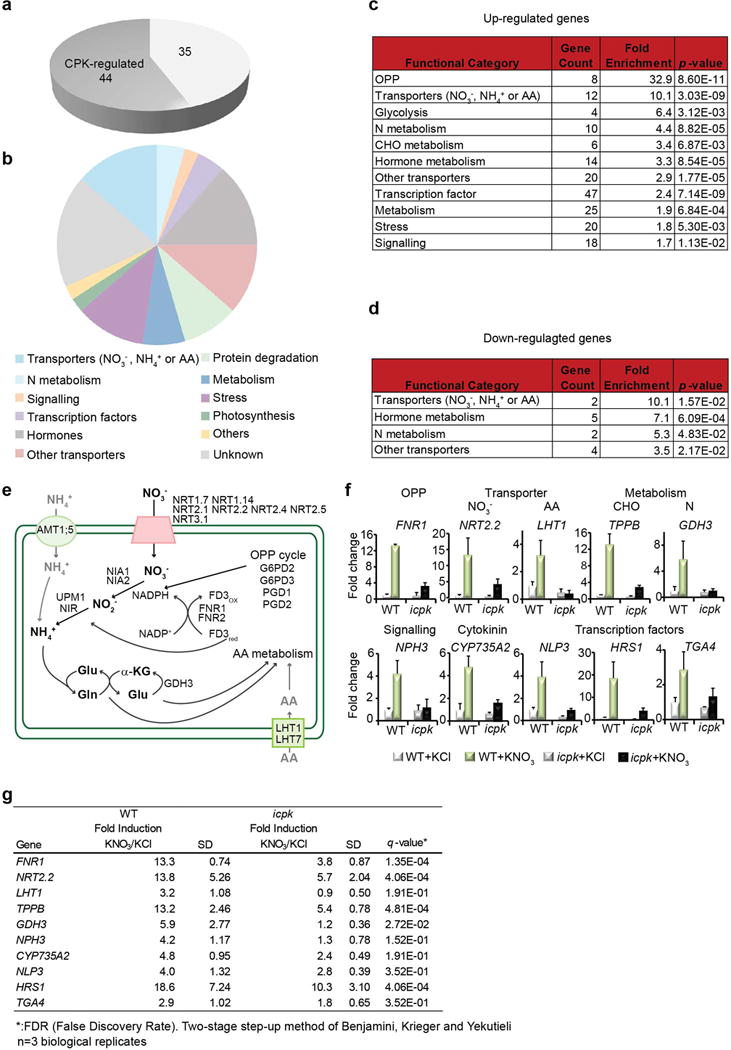
Biological triplicate RNA-seq experiments were performed and analysed with DESeq2. a, Nitrate-CPK down-regulated genes. Dark grey, nitrate-CPK target genes (q ≤ 0.05). b, Classification of nitrate-CPK down-regulated genes. The MapMan functional categories for nitrate down-regulated genes are presented. c, Enriched functional categories of nitrate up-regulated genes. d, Enriched functional categories of nitrate down-regulated genes. The fold enrichment is calculated as follows: (Number of Classified_input_set/Number of total_input_set) / (Number of Classified_reference_set/Number of total_reference_set). The p-value is calculated in Excel using a hypergeometric distribution test. The categories were sorted by fold enrichment with a p ≤ 0.05 cut-off. e, Nitrate-CPK target genes regulate nitrogen transport and metabolism. f, RT-qPCR analyses of nitrate-CPK target genes in eight functional classes in seedlings. KNO3, 10 mM, 15 min. Error bars, s.d., n=3 biological replicates. NITRATE REDUCTASE1/2 (NIA1/2), NIR, NITRATE TRANSPORTER2.1/2.2 (NRT2.1/2.2), G6PD2/3, GLUTAMINE SYNTHETASE (GLN), GLUTAMATE DEHYDROGENASE3 (GDH3), UROPORPHYRINOGEN III METHYLTRANSFERASE1 (UPM1), FERREDOXIN3 (FD3) and FNR1/2, were regulated by CPK10/30/321,3,4,12,17,18,21,32. TF genes, NLP3, HRS1 (HYPERSENSITIVITY TO LOW PI-ELICITED PRIMARY ROOT SHORTENING1) and TGA4 (TGACG MOTIF-BINDING FACTOR 4) were primary nitrate-CPK target genes12,17,18,20,24. g, The fold changes of expression levels of nitrate up-regulated genes in WT and icpk listed in f. The table provided the source data for the histograms presented in f. n=3 biological replicates.
