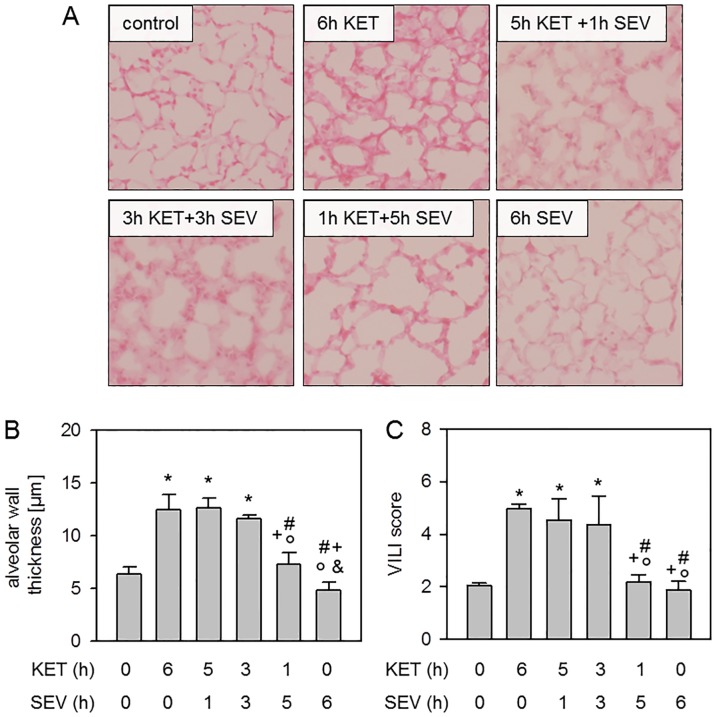
Fig 2. Effect of sevoflurane posttreatment on ventilator-induced lung injury.
Mice were either non-ventilated (control), or they were mechanically ventilated with 12 ml/kg for 6 h either under ketamine + acepromazine (6h KET) or sevoflurane (6h SEV) anesthesia or a combination of both: KET for 5, 3, or 1 h, followed by SEV for another 1, 3, or 5 h as indicated (5h KET + 1h SEV, 3h KET + 3h SEV, 1h KET + 5h SEV). Lung tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Representative pictures are shown for each experimental group as indicated (200x, A). High power fields were randomly assigned to measure alveolar wall thickness (B), and to calculate a ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) score (C). Data represent means ± SD for n = 7/group. ANOVA (Tukey`s post hoc test), *P<0.05 vs. control group; #P<0.05 vs. 6h KET group; +P<0.05 vs. 5h KET + 1h SEV group; °P<0.05 vs. 3h KET + 3h SEV group; &P<0.05 vs. 1h KET + 5h SEV group.