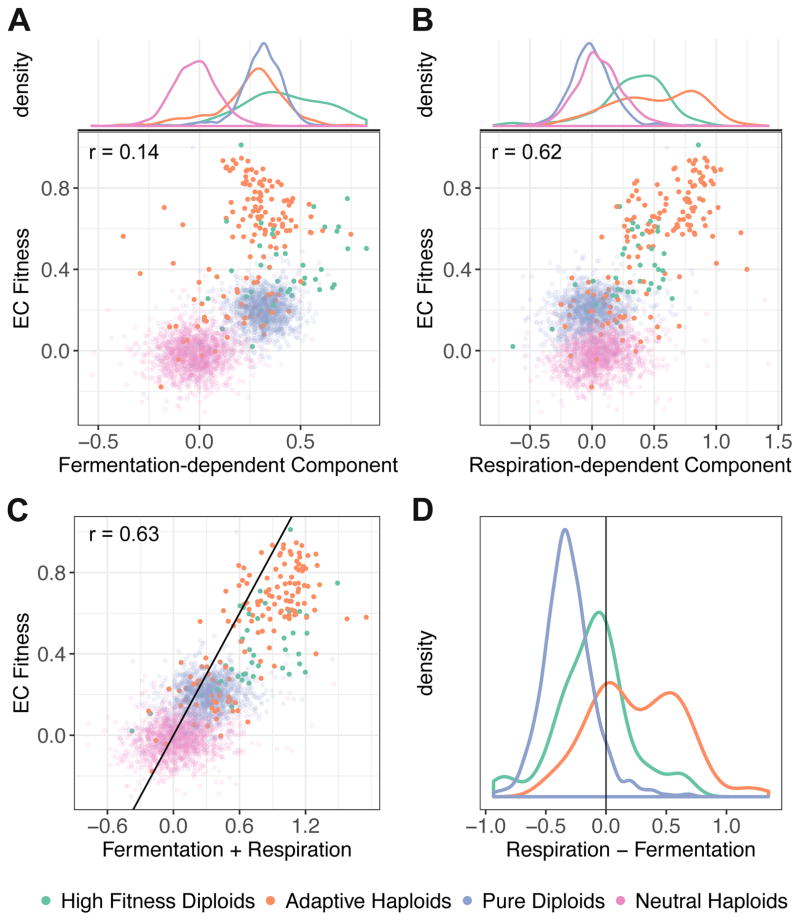
Figure 4. Quantification of fermentation-dependent and respiration-dependent components of fitness in the evolutionary condition, inferred from the variable dilution and cycle length measurements of Figure 3.
(A) Fermentation-dependent component and (B) Respiration-dependent component vs. the per-cycle fitness in the evolutionary condition.
(C) Estimated fitness from combining the fermentation-dependent and the respiration-dependent components against their measured EC fitness. The black line represents y=x. For panels A–C, each dot represents one evolved lineage and is colored by ploidy and adaptive class under the EC; Pearson correlation is calculated for all adaptive lineages.
(D) The difference between the respiration-dependent component and the fermentation-dependent component among four groups of evolved clones.
See also Data S3.