Figure 3.
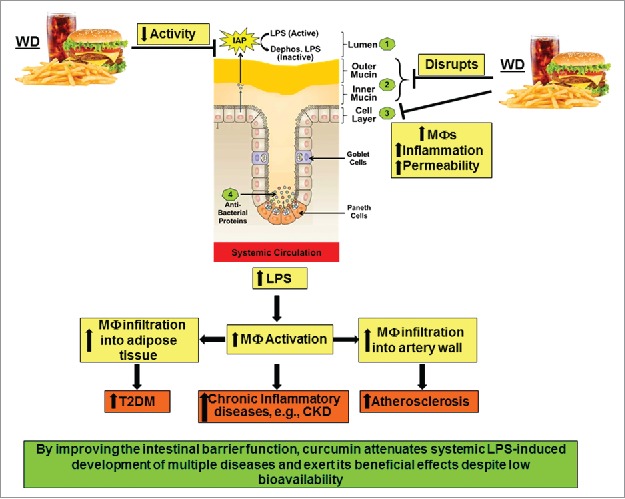
High fat high cholesterol containing Western diet (WD)-mediated disruption of intestinal barrier function and its systemic consequences. WD decreases the activity of intestinal alkaline phosphatase (IAP), disrupts the mucin layers and increase inflammation of intestinal epithelial cell layer by enhancing infiltration of macrophages. Collectively, these effects lead to increased paracellular permeability and lead to an increase in circulating LPS levels. Systemic and tissue macrophages are activated in response to this metabolic endotoxemia and lead to a chronic inflammatory state that underlie the development of multiple diseases including chronic kidney disease (CKD). Infiltration of activated macrophages in adipose tissue or artery wall lead to the development of Type 2 Diabetes (T2DM) or atherosclerosis, respectively.
