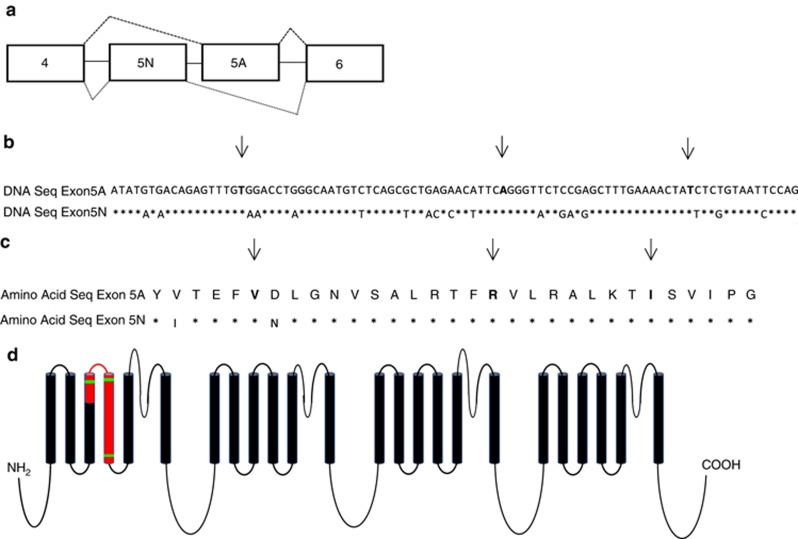
Figure 1.
Exon 5 of SCN8A. (a) Exon 5 is encoded by two sequences in the genome (exons 5 N and 5 A). Only one of the two exons remains in the transcripts after splicing occurs. The nucleotide (b) and amino acid sequences (c) of exons 5 N and 5 A are nearly identical. Asterisks indicate the sites with the same sequence and arrows highlight the sites where a novel disease-causing SCN8A variant was identified in exon 5 A in this study. All disease-causing variants were found at sites where the sequence was identical between exons 5 A and 5 N. (d) Exon 5, highlighted in red, spans two transmembrane domains and a small extracellular region of Nav1.6. The three disease-causing variants, marked in green, were all located in the regions encoding transmembrane-spanning portions of the protein. (Adapted from ref. 4.)