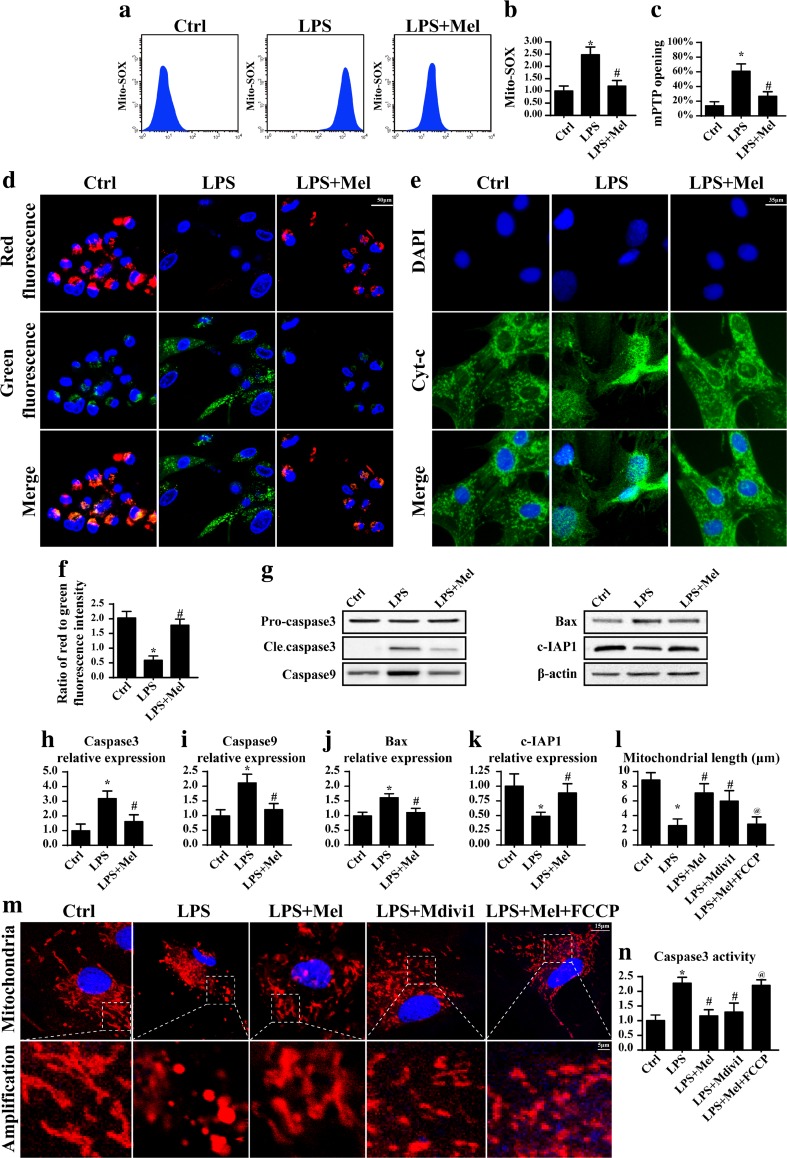
Fig. 2.
Melatonin counteracted caspase9-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis via abating mitochondrial fission. a, b The change of cellular mitochondrial ROS (mROS). Melatonin alleviated the cellular oxidative stress in the presence of LPS. c The change of mitochondrial mPTP opening. Melatonin suppressed the mPTP opening ratio. d The change of mitochondrial membrane potential. The red fluorescence indicated the normal mitochondria with high membrane potential. The green fluorescence was the marker of damaged mitochondria with reduced membrane potential. e The leakage of cyt-c from mitochondria into cytoplasm. f The quantitative expression of mitochondrial membrane potential. g The change of proteins related to the caspase9-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. h–k The quantitative expression of cleaved caspase3, caspase9, Bax, and c-IAP1. l–m The mitochondrial fission was observed via immunofluorescence. More shorter mitochondria appeared in response to LPS treatment. However, melatonin treatment could reverse the mitochondrial length. Mdivi1 and FCCP were the inhibitor and activator of mitochondrial fission, respectively. n Activation of mitochondrial fission could augment the caspase3 activity in the melatonin treatment. *P < 0.05 vs Ctrl group, # P < 0.05 vs LPS group, @ P < 0.05 vs LPS + melatonin group