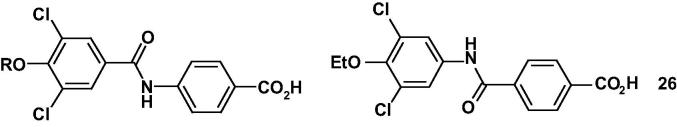
Table 1.
| Subtype-specific transactivationa |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative EC50b |
|||||||
| Compd | RO | RARα | RARβ | β/α ratioc | RARγ | γ/α ratioc | cLogPf |
| 4 | AGN195183 | 11 | 1564 | 141 | 9836 | 867 | 7.2 |
| 5 | EtO | 24 | 1917 | 79 | >3,00,000 | >12,500 | 4.4 |
| 12 | PrO | 15 | 139 | 9.5 | 1196 | 82 | 4.9 |
| 13 | BuO | 84 | 717 | 8.5 | 1477 | 18 | 4.6 |
| 14 | iPrO | 7d | 1417 | 205 | 823 | 119 | 4.7 |
| 16 | tBuO | 7 | 2927 | 426 | 6250 | 909 | 5.1 |
| 15 | 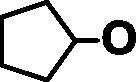 |
10 | 342 | 33 | 4703 | 452 | 5.3 |
| 26 | – | 30 | 355 | 12 | >1,08,000 | >3600 | 4.4 |
| 60 | H | 92d | 642 | 7 | 5000 | 55 | 4.2 |
| 61 | MeO | 30 | 9525 | 318 | 5850 | 195 | 3.9 |
| ATRA | 1.0(1.51 nM)e | 1.0(0.52 nM) e | 1.0(0.22 nM) e | ||||
Transactivation assays for the RAR alpha, beta and gamma receptors were performed using each of the mouse RAR ligand binding domains, Subtype-specific activity is expressed in terms of relative EC50 which is the concentration of retinoid required to produce 50% of the maximal observed response, normalised relative to that of ATRA.
Mean EC50 for each compound divided by the mean EC50 of ATRA. Values were obtained from three separate experiments. Errors in these assays are approximately 20% of the mean values.
The relative EC50 ratios of α to β and α to γ.
Compound behaves as a partial agonist relative to the amplitude of the normalizing ATRA output.
Mean of ATRA EC50 (nM).
cLog P values were calculated in ChemDraw.