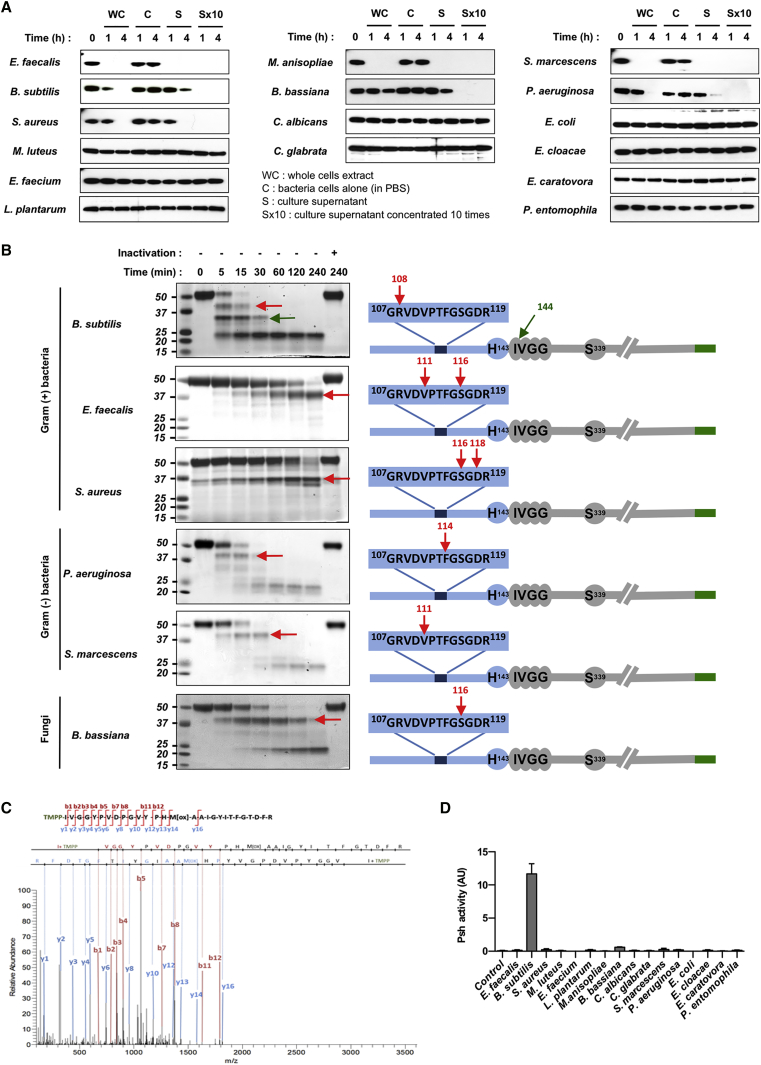
Figure 3.
Hydrolysis of rpro-Psh by Microbial Extracellular Proteases
(A) rpro-Psh labeled with a C-terminal HisTag (0.2 μg/μL) was incubated at 29°C with whole-cell cultures of microorganisms grown to early stationary phase and microorganism cells suspended only in PBS, cell-free culture medium (supernatant), or the same medium (supernatant) concentrated ten times. After 1 or 4 hr, 1 μg aliquots were removed and the reaction was stopped at 100°C for 5 min. Residual rpro-Psh was visualized by western blot with an anti-6HisTag antibody. Representative results of at least two independent experiments.
(B) rpro-Psh was incubated under the same conditions with cell-free media (supernatant). At various time points, 5 μg of proteins were removed and the reaction was stopped at 100°C for 5 min. Controls were performed after pre-inactivation of the media for 5 min at 100°C. Hydrolysis products were visualized by Coomassie blue staining after SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. Identifications of neo-N-terminal peptides were determined by nano-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (nano-LC-MS/MS) analysis after in-gel protein N-terminal chemical derivatization method using TMPP reagent. Arrows indicate identified N-terminal extremities.
(C) Characterization of TMPP-derivatized peptide of the expected N-terminal extremity of the catalytic domain by MS/MS fragmentation spectrum. The corresponding MS/MS fragmentation table is presented as Table S4.
(D) Cell-free supernatant of S2 cells expressing rpro-Psh (200 μL) was incubated in 0.1 M TrisHCl buffer (pH 8) with 200 μL of cell-free medium from microorganism cultures (final volume, 600 μL). After 1 hr, proteolytic activity of the generated rpro-Psh hydrolysis products was determined on the fluorogenic substrate Z-Arg-AMC for 30 min at 29°C in 0.1 M TrisHCl buffer (pH 8) supplemented with 5 mM CaCl2.