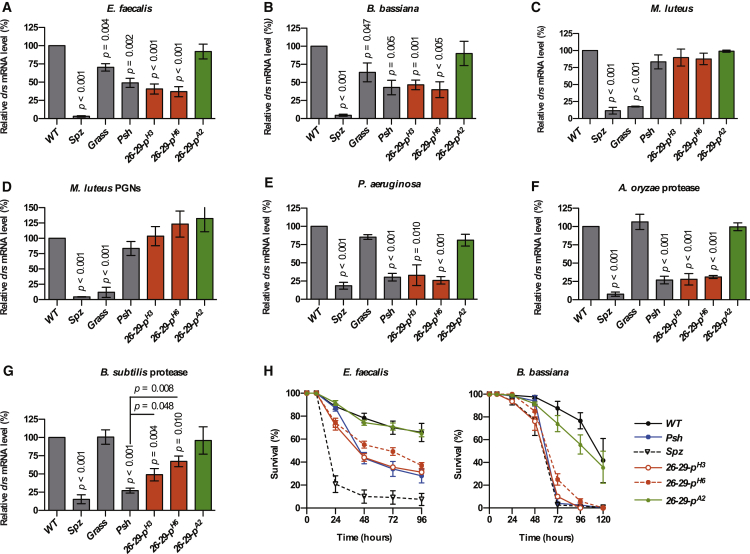
Figure 6.
Cathepsin 26-29-p Is Required for Psh Sequential Activation
Two null mutant alleles of the 26-29-p gene (26-29-pH3 and 26-29-pH6) were generated by imprecise P-element excision resulting in deletions spanning transcriptional start site and the first two exons of the gene. A clean excision restoring expression of wild-type 26-29-p was used as control (26-29-pA2) (Figure S4).
(A–G) Flies of the indicated genotype were challenged by septic injury with E. faecalis (OD600 = 1) (A), M. luteus (OD600 > 200) (C), or P. aeruginosa (OD600 = 1) (E); by natural infection with B. bassiana (B); or by injection of M. luteus peptidoglycans (D), A. oryzae protease (F), or B. subtilis protease (G). After 24 hr at 29°C (16 hr for the purified proteases), flies were collected and drs gene expression was monitored by qRT-PCR in total RNA extracts. Ribosomal protein 49 (Rp49) mRNA was used as reference gene. Results were normalized to the value obtained with the wild-type flies. Data represent means ± SEs of three independent experiments, each containing three groups of ten flies (five males and five females). p values obtained from one-way ANOVA test are indicated on the graphs.
(H) Survival of adult flies challenged with E. faecalis by septic injury (OD600 = 1) or with B. bassiana by natural infection. Data represent means ± SEs of three independent experiments, each containing three groups of 20 flies (10 males and 10 females). Log-rank statistical analyses are presented as Table S5.