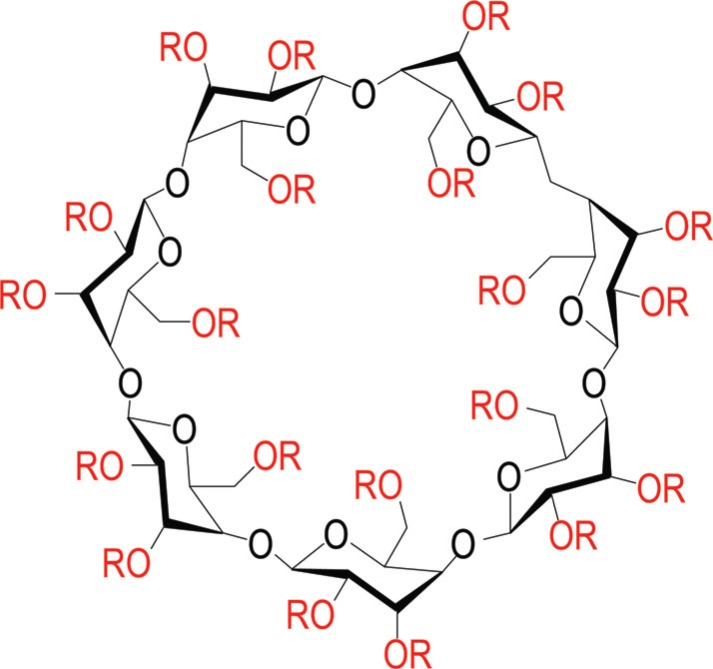
Fig. (1).
Structure of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD). There are 21 sites (red) on the large β cyclodextrin ring that are potential substitution sites for condensation with propylene oxide to yield various species of HPβCD with different degrees of substitution, depending upon how many sites are substituted. HPβCD products exist as complex mixtures of different chemical species with varying degrees of substitution, not as a single chemical structure with set numbers and positions of substitutions. Variations in proprietary production processes lead to differences in composition of these mixtures. Consequently, different cyclodextrin products should not be expected to have the same formulation, biological activity, and/or clinical safety/efficacy profile. R = H or CH2-CHOH-CH3. (The color version of the figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).