Figure 3.
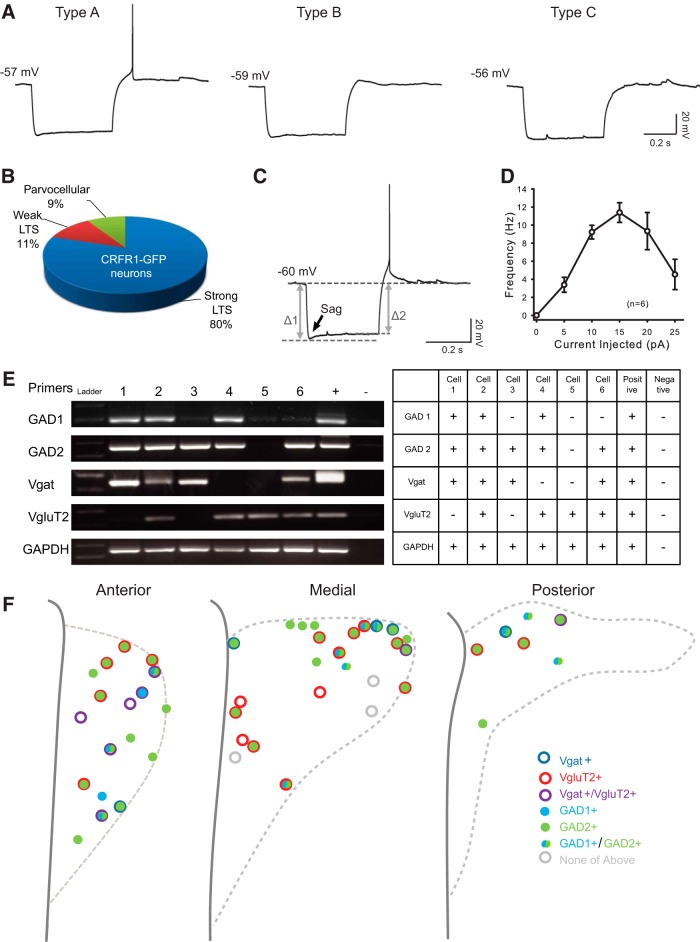
Electrophysiological and molecular properties of CRFR1-GFP neurons in the PVN. A, Representative responses of CRFR1-GFP neurons to a negative current injection step (−100 pA, 500 ms). B, Eighty percent of the CRFR1-GFP neurons fire at least one action potential in response to a −100 pA hyperpolarization current (type A), 11% express a small “hump” (type B), and 9% show no LTS (type C). C, Majority CRFR1-GFP neurons express a small sag in response to a hyperpolarization current. The arrow points out the “sag,” indicative of the presence of hyperpolarization-activated channels. D, A current–frequency plot showing high spike frequency adaptation of CRFR1-GFP in response to a series of depolarization currents. E, A representative image, and summary table of single-cell reverse-transcription PCR results. F, Summary and location information for 50 identified PVN CRFR1-GFP neurons.