Figure 6.
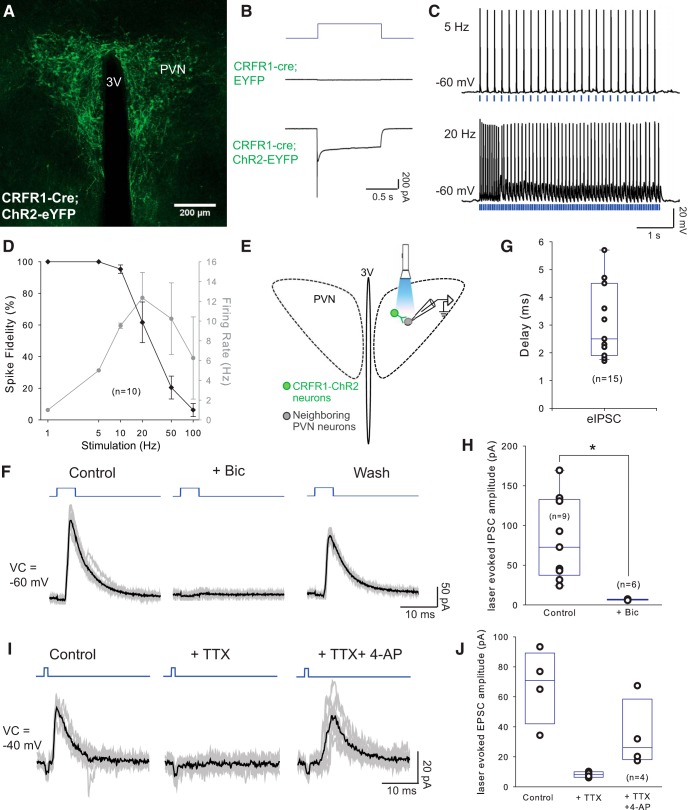
PVN-CRFR1 neurons make local projections within the nucleus. A, Selective expression of ChR2-YFP in CRFR1-Cre neurons in the PVN. B, Representative traces of photocurrents recorded in CRFR1 neurons. In CRFR1 neurons expressing ChR2, 1 s photostimulation induced typical ChR2-mediated currents (bottom trace), whereas photostimulation with the same intensity and duration failed to induce photocurrents in the CRFR1 neurons infected with control virus (middle trace). C, Sample traces of action potential firing from a CRFR1-ChR2 neurons with 5 and 20 Hz optical stimulation (laser duration 1–5 ms), note the slowing of firing with 20 Hz stimulation. D, Entrainment of CRFR1-ChR2 neurons to direct optical stimulation: percentage change in spike fidelity and ChR2-mediated CRFR1 neurons firing (n = 10). E, Schematic experimental design. Laser-evoked postsynaptic responses were recorded in neighboring PVN neurons. (F) Representative traces from a neighboring neuron in the PVN, showing laser-evoked IPSCs, which are blocked by Bic and are restored after washout. Blue, Photostimulation; gray lines, individual traces; dark lines, averaged traces. G, Delay of laser-evoked eIPSCs from PVN neurons (n = 15). H, Summary histogram of eIPSCs in the PVN, which is blocked by selective GABAA antagonist bicuculline (40 μm; n = 6; p < 0.05, paired Student's t test). I, Representative trace of a laser-evoked IPSC, which is blocked by TTX and rescued by 4-AP. Blue, Photostimulation; gray lines, individual traces; dark lines, averaged traces. J, Summary histogram of eIPSCs blocked by TTX and rescued by 4-AP (n = 4). *p < 0.05.