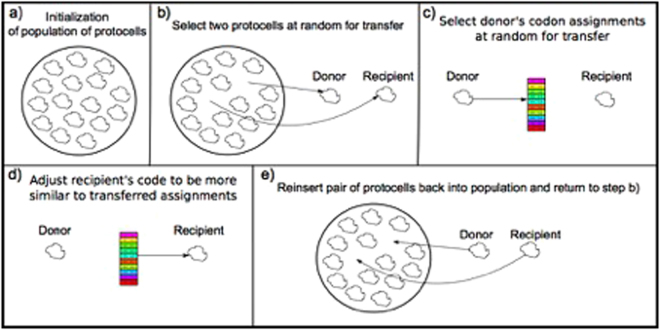
Figure 3.
A model of communal evolution of the genetic code. (a) A small group of protocells is initialized such that their ‘black box’ primitive translation systems encode random genetic codes consisting of few amino acids. Then the ‘iterative learning’ cycle begins. (b) Two protocells are randomly selected for horizontal transfer of a fragment of the donor’s genetic code to the recipient. (c) A small subset of codon assignments is randomly chosen and transferred; occasionally, codon assignment inaccuracies can occur in the transferred components. (d) The recipient adjusts its genetic code to be more like the donor’s code according to the received assignments. (e) The process of horizontal transfer is completed. Then the cycle starts again by going back to (b).