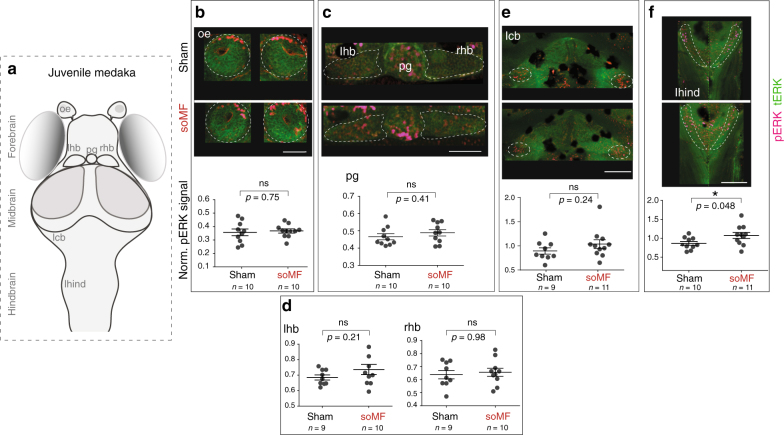
Fig. 4.
Increased number of pERK-positive neurons found in juvenile medaka hindbrain upon stimulation with a slowly oscillating magnetic field. a Schematic of medaka brain, dorsal view, anterior up. The major anatomical divisions into forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain are indicated. oe olfactory epithelium, pg pineal gland, hb left habenula, rhb right habenula, lcb lateral cerebellum, lhind lateral hindbrain. b–f Upper panels show confocal images (maximum z-projections) of the different brain areas of interest stained against phosphorylated ERK (pERK, magenta) and total ERK (tERK, green) in juvenile medaka exposed to soMF or control condition (sham). Scale bars: 50 μm (b, c), 100 μm (d, e, f). Lower panels show the corresponding quantifications of the normalized pERK signals (pERK/tERK). The plots show mean and standard error (±SEM). A t-test (two-tailed) with Welch’s correction for unequal variances was used and p values adjusted for multiple comparison by controlling the false discovery rate (FDR) at 0.05 alpha level of significance are reported. Dark spots in the images correspond to sparse pigments present in the Cab strain. Signals from regions with prominent pigmentation were not quantified