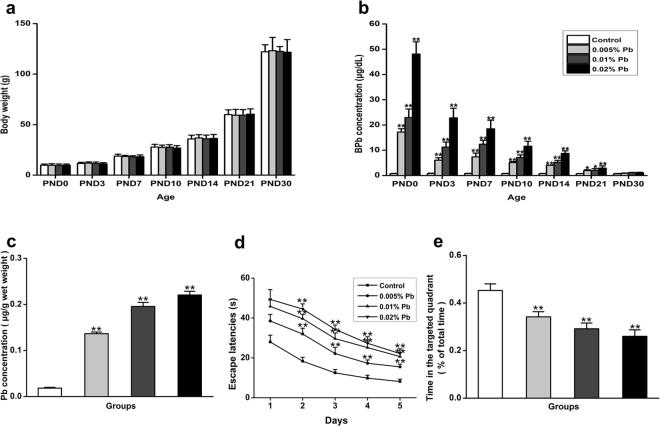
Figure 1.
Pb accumulation in the hippocampus and its effect on learning and memory on PND30 rats. Morris water maze test was performed to detect learning and memory ability in four groups of animals: Control, 0.005% Pb, 0.01% Pb and 0.02% Pb. (a) Body weights (N = 8 per group) and (b) blood-lead-levels (BLLs) (N = 8 per group) were measured at postnatal day (PND) 0, 3, 7, 10, 14, 21 and 30. (c) Hippocampal Pb levels (N = 8 per group) and (d,e) the water maze test (N = 8 per group) were only measured at PND 30. Test results showed that with increased Pb exposure, the escape latencies were positively correlated, and time spent in the targeted quadrant at the test day were negative correlated. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.