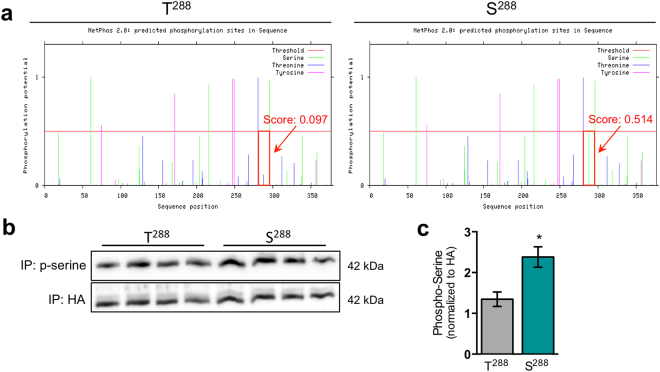
Figure 5.
Substitution of serine for threonine at position 288 (S288) in ZnT2 leads to ZnT2 hyperphosphorylation. (a) Graphical representation of potential phosphorylation sites (serine, threonine and tyrosine) in wild-type ZnT2 (T288; left) and ZnT2 variant with a threonine to serine substitution (S288; right) as inferred from NetPhos 2.0. Green line represents potential phosphorylated serine residues; blue line represents potential phosphorylated threonine residues; pink line represents potential phosphorylated tyrosine residues; red horizontal line indicates threshold for modification potential; score indicates predicted phosphorylation potential score. (b) Representative immunoblot of phosphorylated serine in immunoprecipitates (IP) from MECs expressing T288 or S288. HA was used as normalization and input control. Cropped blots are displayed and full-length blots can be found in Supplementary Fig. S6a,b. (c) Quantification of serine phosphorylation. Data represent mean p-serine/HA ratio ± SD, n = 6 samples/genotype, from two independent experiments; p < 0.05*.