Figure 6.
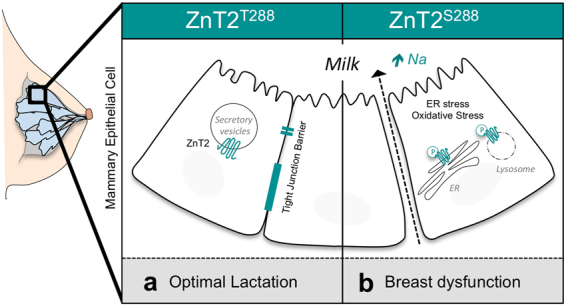
Model comparing MEC functions of wild-type ZnT2 (T288) and the ZnT2 variant (S288) during lactation. (a) Optimal lactation is achieved through tight regulation of milk secretion, MEC polarity and barrier integrity. During lactation, wild-type ZnT2 (T288) imports zinc into secretory vesicles in MECs, which is critical for secretory differentiation and secretory activation. (b) However, a common hyperphosphorylated ZnT2 variant (S288) is retained in the ER and lysosomes, leading to increased ER and lysosomal Zn accumulation, ER and oxidative stress, defects in tight junction formation and paracellular barrier formation, resulting in sodium leakage into milk.
