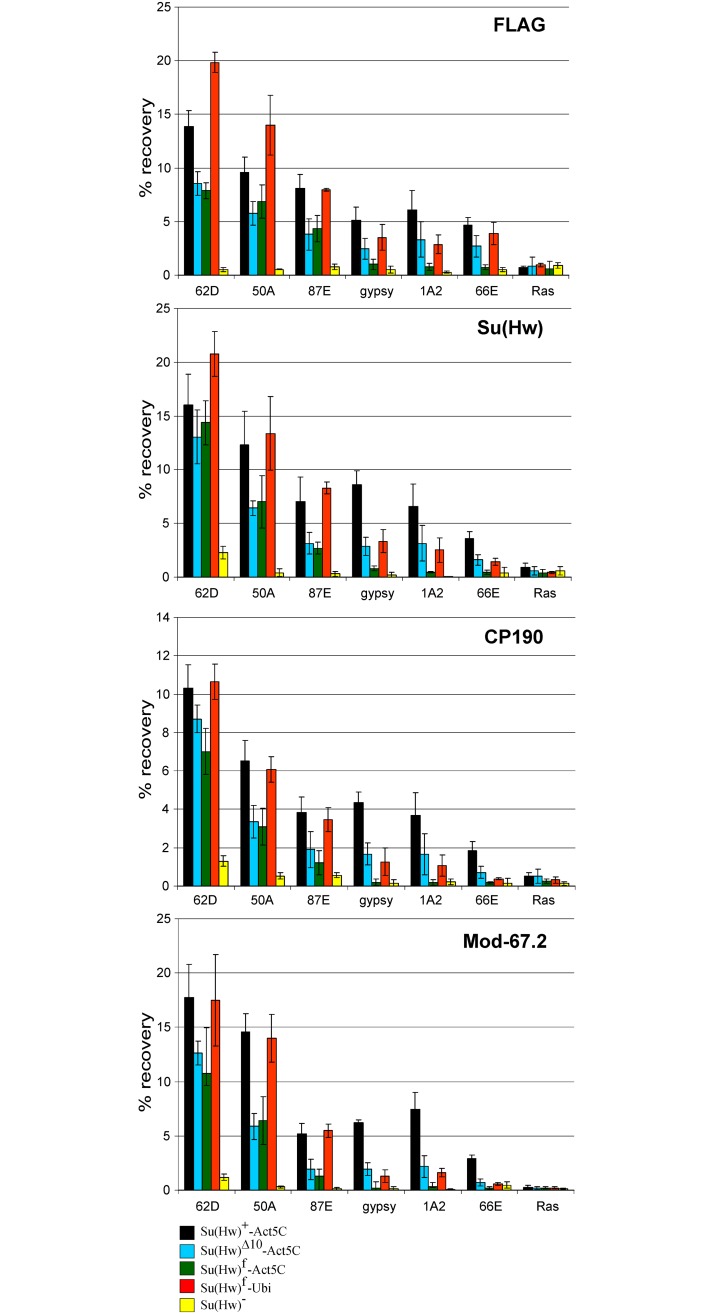
Fig 3. Evaluation of binding of the insulator protein in the mod(mdg4)+ transgenic lines.
Variants of the Su(Hw) protein were expressed in the y2scD1ct6; P{Su(Hw)}-38D/P{Su(Hw)}-38D; su(Hw)v/su(Hw)e04061 lines, where P{Su(Hw)} are Su(Hw)+-Act5C –P{w+;WAB-Su(Hw)1-945-FLAG}/ P{w+;WAB-Su(Hw)1-945-FLAG}; Su(Hw)Δ10-Act5C –P{w+;WAB-Su(Hw)Δ10-FLAG}/ P{w+;WAB-Su(Hw)Δ10-FLAG}; Su(Hw)f-Act5C –P{w+;WAB-Su(Hw)f -FLAG}/ P{w+;WAB-Su(Hw)f -FLAG}; Su(Hw)f-Ubi–P{w+;UbqW-Su(Hw)f -FLAG}/ P{w+;UbqW-Su(Hw)f -FLAG}. The y2scD1ct6; su(Hw)v/su(Hw)e04061 line is designated as Su(Hw)−. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was performed at the selected Su(Hw) regions. The ras64B coding region (Ras) was used as a negative control. The percent recovery of immunoprecipitated DNA (Y axis) was calculated relative to the amount of input DNA. Error bars indicate standard deviation of three independent biological replicates.