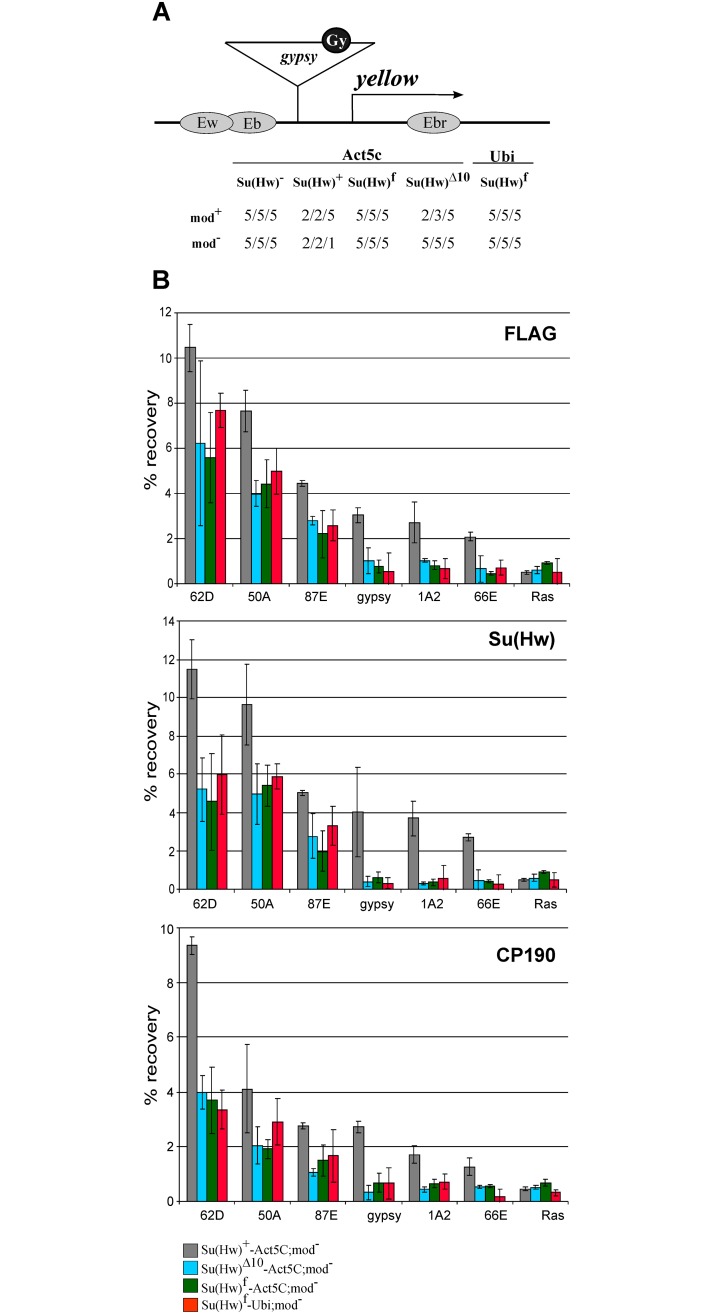
Fig 4. Effects of the su(Hw) mutations on the activity of gypsy insulator in the mod(mdg4)u1 background.
(A) Effects of the mod(mdg4)u1 mutation on yellow expression in transgenic lines. A schematic of the y2 allele (drawn not to scale): the yellow wing (Ew) and body (Eb) enhancers are shown as partially overlapping gray ovals; the bristle enhancer (Ebr), as a gray oval in the yellow intron; the transcription start site is indicated by an arrowhead. The gypsy insertion is shown as a triangle with the black circle (Gy) marking Su(Hw) binding sites. Analysis of the transgenic lines was performed in the y2scD1ct6; mod(mdg4)+/mod(mdg4)+ background (mod+) or in the y2scD1ct6; mod(mdg4)u1/mod(mdg4)u1 background (mod−). Numbers in the "mod+" and "modȢ" lines indicate a relative level of yellow expression in the body cuticle/wing blades/bristles, which ranged from 2 (pigmentation as in the y2 allele) to 5 (pigmentation as in the wild-type flies). (B) ChIP-qPCR analysis of Su(Hw), Mod-67.2, and CP190 binding at the mid-pupal stage in the transgenic lines expressing different variants of Su(Hw) in the y2scD1ct6; P{Su(Hw)}-38D/P{Su(Hw)}-38D; su(Hw)v mod(mdg4)u1/ su(Hw)e04061 mod(mdg4)u1 lines (mod− in designations of the lines). The abbreviations of transgenes P{Su(Hw)} are as in Fig 3. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was performed on the intergenic regions bound by Su(Hw). PCR products were amplified from two separate immunoprecipitates of three different chromatin preparations. The ras64B coding region (Ras) was used as a control devoid of Su(Hw) binding sites. The recovery percentage of immunoprecipitated DNA (Y axis) was calculated relative to the amount of input DNA. Error bars indicate standard deviation of three independent biological replicates.