Figure 1.
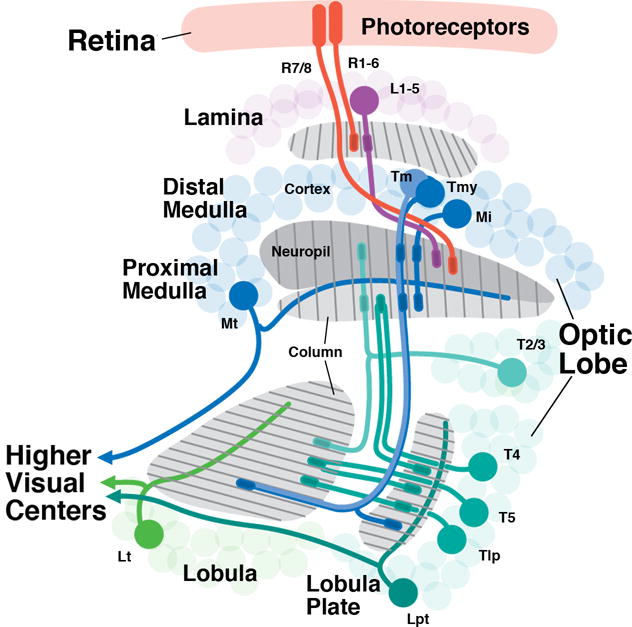
Overview of neuronal connectivity in the Drosophila visual system. Photoreceptors (red) are located in the retina and project in a precise retinotopic manner to the visual processing center of the brain, the optic lobe. The optic lobe has four synaptic compartments (from distal to proximal): lamina, medulla, lobula, and lobula plate. The medulla synaptic layer is subdivided to the distal and proximal region separated by the serpentine layer. R1-R6 photoreceptors terminate in the lamina while R7-R8 terminate in the medulla. Lamina interneurons (L1-5; purple), targeted by R1-R6 project to the distal medulla; medulla local interneurons (medulla intrinsic neurons; Mi) interconnect the distal and proximal medulla; projection neurons (Tm, Tmy) connect to the lobula and lobula plate. Columnar neurons also connect lobula and lobula plate (Tlp), and lobula/lobula plate to the medulla (T2-5). Large tangential neurons of the medulla (Mt), lobula (Lt) and lobula plate (Lpt) transmit processed visual information to the central nervous system. Several types of local neurons interconnecting neighboring medulla columns (Dm, Pm), projection neurons (T1, Y), as well as columnar projections neurons of the lobula are omitted.
