Figure 2.
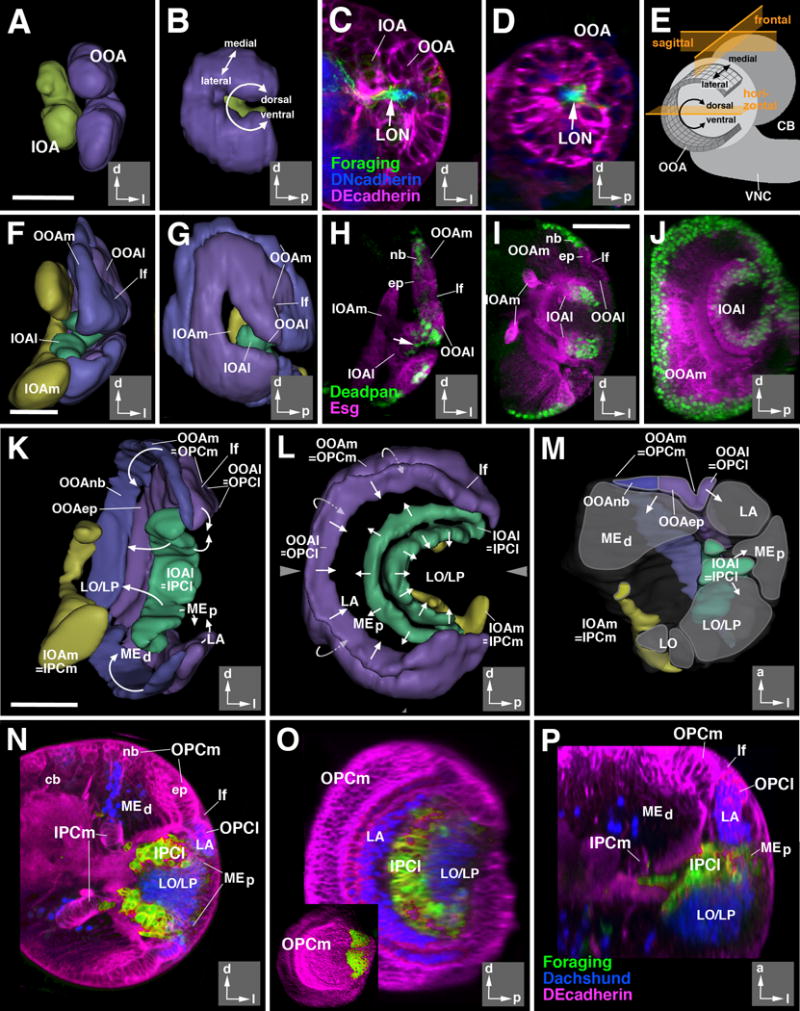
Architecture of the larval optic lobe primordium. 3D digital models and confocal sections of the developing larval optic lobe at the 2nd instar (32hr; A-D), early 3rd instar (72hr; F-H), and late 3rd instar (120hr; I-P) larval stages. Models present two different views for all three stages: posterior view (A, F, K), and lateral views (B, G, L). Insets at lower right corner of panels delineate orientation (a anterior; d dorsal; l lateral; p posterior). The outer optic anlage (OOA; for late stages called outer proliferation center, OPC) is shown in purple (epithelial; lateral part; OOAep) and blue (neuroblasts; medial part; OOAnb), respectively. The inner optic anlage (IOA; later stages: IPC) is shown in yellow (epithelial medial part; IPCm) and green (mesenchymal lateral part; IPCl). Panel (M) shows a cutaway model of the optic lobe of a late larva. In this model, the optic lobe is digitally cut along a horizontal plane [indicated by arrowheads in adjacent panel (L)], and a dorsal view of the cut surface of the bottom part is presented. Areas shaded in gray correspond to the primordia of the optic ganglia (LA lamina; LO lobula; LP lobula plate; MEd distal medulla; MEp proximal medulla) generated by the optic proliferation centers. Arrows in (K-M) indicate the direction in which optic proliferation centers convey postmitotic neurons. Drawing in panel (E) presents a schematic lateral view of larval brain (CB central brain; VNC ventral nerve cord) which illustrates the shape and location of the epithelial outer optic anlage. Note the curvature of the dorso-ventral axis which places the dorsal and ventral edge of the OOA close to each other. The three planes of sectioning used in this and the following figures (sagittal or parasagittal, frontal, horizontal) are indicated in orange. (C-D, H-J, N-P): z-projections of confocal sections (approximately 15-20 μm thickness) of the optic lobe; (C, F, H, I, N) are frontal sections, (D, J, O) are parasagittal sections, and (P) is a horizontal section. The epithelium of the optic anlagen is either marked by DE-Cadherin (in red; C-D, N-P) or mCD8-GFP driven by esg-Gal4 (in red; H-J). Neuroblasts are marked by Deadpan (in green, H-J). Larval optic neuropil (LON) is marked by foraging (forNP0079-Gal4>UAS-mCD8-GFP; green in C-D), and the central brain (CB) neuropil is marked by Discs-large (in blue, C-D). In panels (N-P) Dachshund (blue) labels neural precursors of the lamina (LA; Pineiro et al., 2014) and the T4/T5 neurons of the lobula/lobula plate (LO/LP). forNP0079-Gal4 >UAS-mCD8-GFP; green) exclusively labels the lateral domain of the inner proliferation center (IPCl). Inset in (O) shows expression of a wingless reporter (wg-Gal4>UAS-mCD8-GFP) in the dorsal and ventral tips of the outer proliferation center (OPC).
Abbreviations used in this and all following figures: cb central brain; cl medulla column; cor cortex; ep epithelium; IOA inner optic anlage; IOAl lateral part of inner optic anlage; IOAm medial part of inner optic anlage; IPCl lateral domain of inner proliferation center; IPCm medial domain of inner proliferation center; L columnar lamina neurons; LA lamina; lf lamina furrow; LO lobula; LON larval optic neuropil; LP lobula plate; Lt lobula tangential neurons; mc medulla cortex; ME medulla; MEd distal medulla; MEp proximal medulla; Mt medulla tangential neurons; nb neuroblast; np neuropil; OOA outer optic anlage; OOAep epithelial domain of the OOA; OOAl lateral part of outer optic anlage; OOAm medial part of outer optic anlage; OOAnb neuroblast domain of the OOA; OOC outer optic chiasm; OPCl lateral domain of outer proliferation center; OPCm medial domain of outer proliferation center; T2-5 classes of columnar T-shaped neurons interconnecting lobula complex and medulla; Tlp columnar trans lobula plate neurons; Tm columnar transmedulla neurons; Tmy columnar transmedulla y-shaped neurons; TMP transient medulla plexus; VLP ventrolateral protocerebrum; VNC ventral nerve cord.
Bars: 20 μm (A-D; F-H); 50μm (I-J; K-P)
