Figure 2. TGF-β1 attenuates expression of Claudin-7.
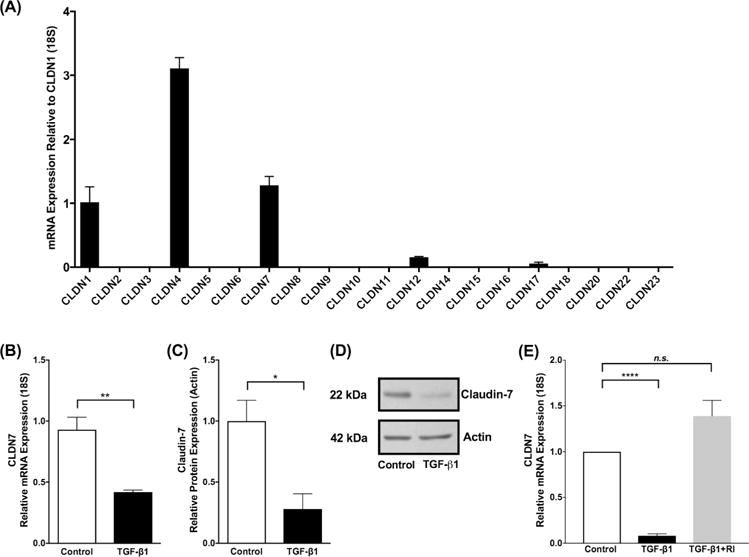
(A) Claudin mRNA expression in immortalized human esophageal epithelial (EPC2-hTERT) cells as mean fold change relative to CLDN1. CLDN 1, 4 and 7 were the predominantly expressed claudin mRNAs in the esophageal epithelium differentiated and stratified in 3D-ALI culture. (B) Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) exposure (10 ng/ml) led to no significant effect on expression of selected epithelial barrier molecules, but decreased expression of CLDN7 mRNA and (C) claudin-7 protein in EPC2-hTERT cells at 3D-ALI (N=3, *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01). (C) Representative western blot demonstrates decreased claudin-7 protein in the presence of TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml). (E) EPC2-hTERT cells exposed to TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) leads to attenuation in claudin-7, however when exposed to TGF-β type 1 receptor inhibitor (TGF-β RI) (5μm) prior to TGF-β1, cells were protected from the attenuation in claudin-7, indicating that the TGF-β1 pathway directly influences the attenuation of claudin-7 (N=4, ****p≤0.0001).
