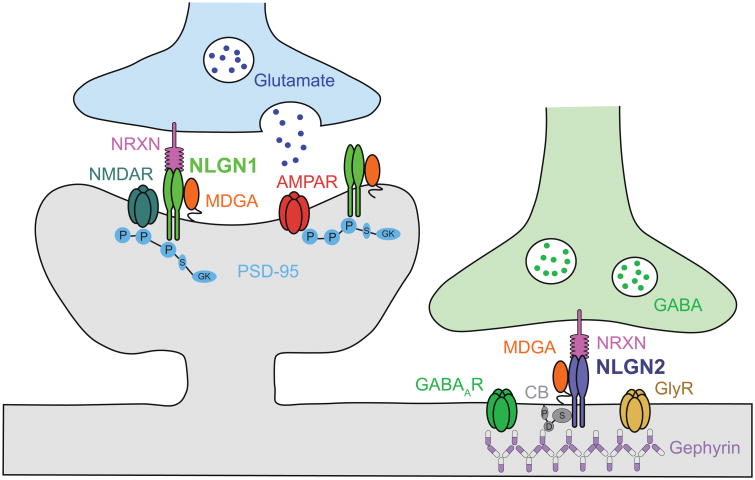
Figure 2.
Neuroligin 1 (NLGN1) and NLGN2 cell adhesion molecules at excitatory and inhibitory synapses, respectively. NLGN1 and NLGN2 are enriched are postsynaptic membranes, and their extracellular domains adhere to distinct isoforms of neurexins (NRXN) at presynaptic membranes. Intracellularly, NLGN1 binds to the scaffolding protein postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD95), and regulates the synaptic localization of glutamate receptors (GluR) α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPARs) and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs). NLGN2 forms a complex with collybistin (CB) and gephyrin (GPHN) and regulate the synaptic localization of GABA receptors (GABAR). The cell-surface molecules MAM domain-containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor proteins (MDGAs) form post-synaptic cis-complexes with NLGN1 and NLGN2, and negatively regulate their trans-synaptic adhesion with NRXNs [60-62]. Additional protein abbreviations: GlyR, glycine receptor; P, PDZ binding domain; S, Src homology domain (SH3 domain); GK, guanylate kinase domain; D, Dbl homology domain; P, Pleckstrin homology domain (Adapted from Bemben et al., 2015 [48]).