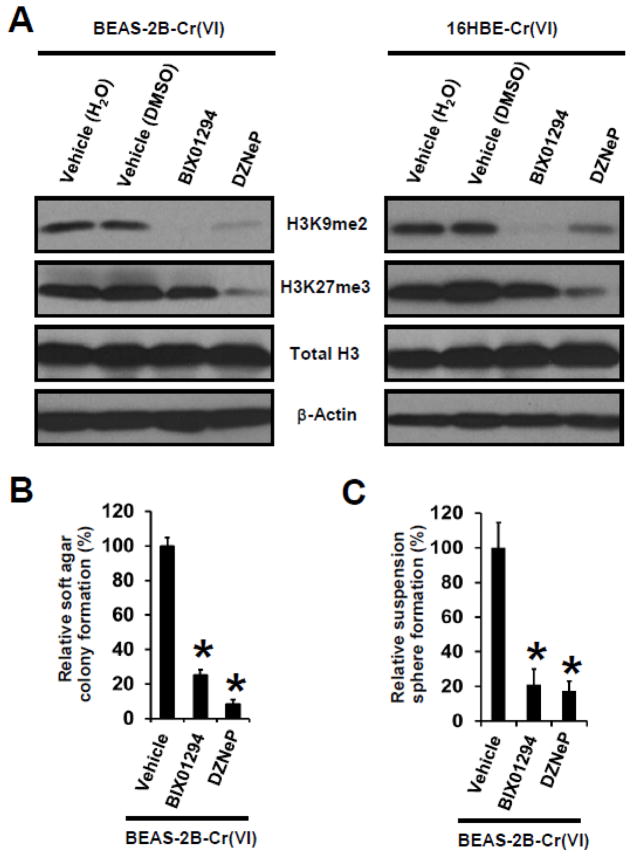
Fig. 3. Pharmacological inhibition of HMTases in Cr(VI)-transformed cells abolishes their H3 repressive methylation marks and reduces their transformed phenotypes.
(A) Representative Western blot images for the analysis of histone H3 repressive methylation marks in Cr(VI)-transformed cells. Cells were treated with vehicle control, a G9a inhibitor BIX01294 (2.5 μM) or an EZH2 inhibitor DZNeP (0.25 μM) for 72 h, and harvested for Western blot analysis. (B) Quantitation of effects of inhibition of G9a or EZH2 on soft agar colony and suspension culture sphere formation by Cr(VI)-transformed cells. Cells were treated with vehicle control, a G9a inhibitor BIX01294 (2.5 μM) or an EZH2 inhibitor DZNeP (0.25 μM) for 72 h, and harvested for soft agar colony and suspension culture sphere formation assay. Results are expressed as relative colony or sphere formation compared to vehicle-treated BEAS-2B-Cr(VI) cells (100%). Data are presented as mean ± SD (n=3). *p< 0.05, compared to vehicle-treated group. Similar results were obtained in two additional experiments.