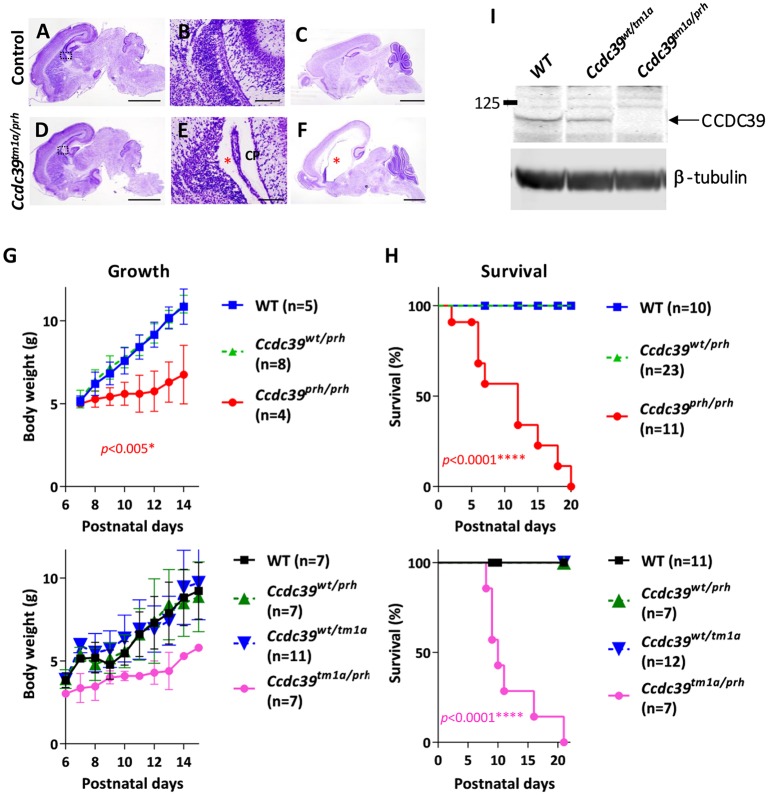
Fig. 2.
Ccdc39tm1a/prh mice phenocopy Ccdc39prh/prh mice. (A-F) Nissl staining of sections of P0 control (A,B) and Ccdc39tm1a/prh (D,E) mutant mouse brains. The Ccdc39tm1a/prh mice show moderate ventriculomegaly (asterisk in E), reproducing the brain phenotype of Ccdc39prh/prh mice at P0. Nissl staining of sections of P9 Ccdc39tm1a/prh (F) and control (C) mouse brains. Ccdc39tm1a/prh mice developed severe hydrocephalus with substantially enlarged lateral ventricles (asterisk in F). Body weight (G) and survival rate (H) of postnatal Ccdc39tm1a/prh mice recapitulated the phenotypes of Ccdc39prh/prh mice. The failure of the Ccdc39tm1a allele to complement the Ccdc39prh mutation is consistent with prh being an allele of Ccdc39. P values are generated in the comparisons of null mutant with wild type. (I) Western blotting with CCDC39 antibody on P8 brain lysate from Ccdc39wt/wt (WT), Ccdc39wt/tm1a and Ccdc39tm1a/prh mice. β-Tubulin, loading control. CP, choroid plexus. Scale bars: 2 mm (A,C,D,F), 0.5 mm (B,E).