Fig. 4.
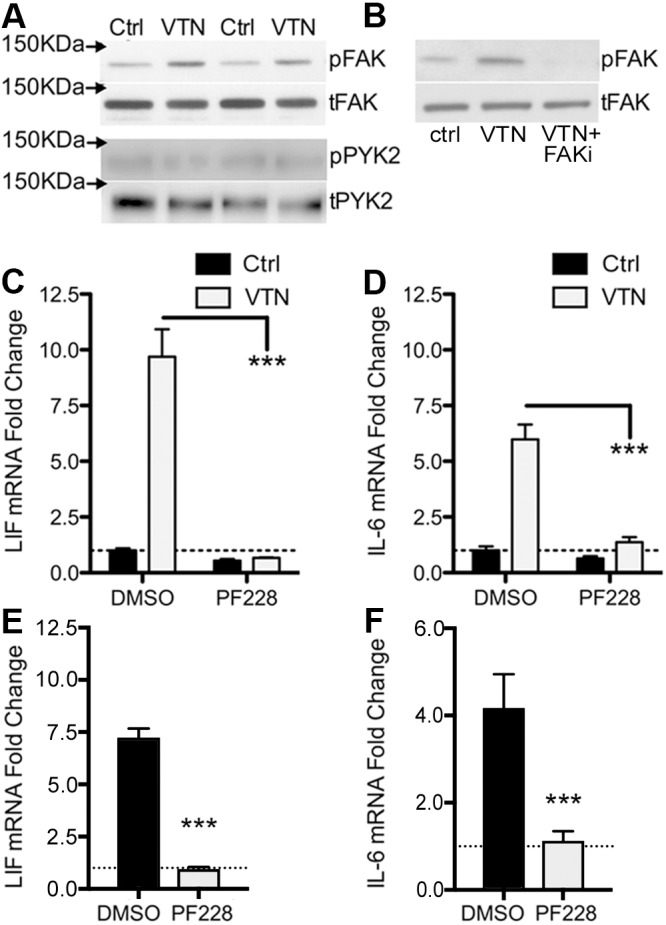
FAK inhibition abolishes VTN mediated LIF and Il-6 induction. C6 cells were seeded onto VTN-coated tissue culture plates (50 µg/ml) or non-treated control (Ctrl) plates and maintained for 4 h. (A) In these conditions, VTN stimulates phosphorylation of Y397-FAK (pFAK) but not of PYK2 at the corresponding Y402 residue (pPYK2), as shown in western blots. Loading controls are total FAK (tFAK) and PYK2 (tPYK2). Two representative lanes per group from three independent experiments are shown (n=3). (B) FAK antagonist PF573228 (10 µM, FAKi) completely blocked the VTN-stimulated pY397-FAK formation when added immediately after cells were seeded (n=3). In addition, the FAK inhibitor PF573228 (PF228) completely abolished VTN-induced LIF (C) and IL-6 (D) gene expression as measured by RT-qPCR. Control (Ctrl) vehicle is 0.1% DMSO (mean±s.e.m.; n=4 independent experiments). In further experiments, C6 cells were cultured in serum-free medium for 24 h before VTN was added directly to medium with or without FAK inhibition (PF228), (E) LIF and IL-6 (F) induction by VTN was also completely abolished by FAK inhibition in these conditions (mean±s.e.m.; n=3).
