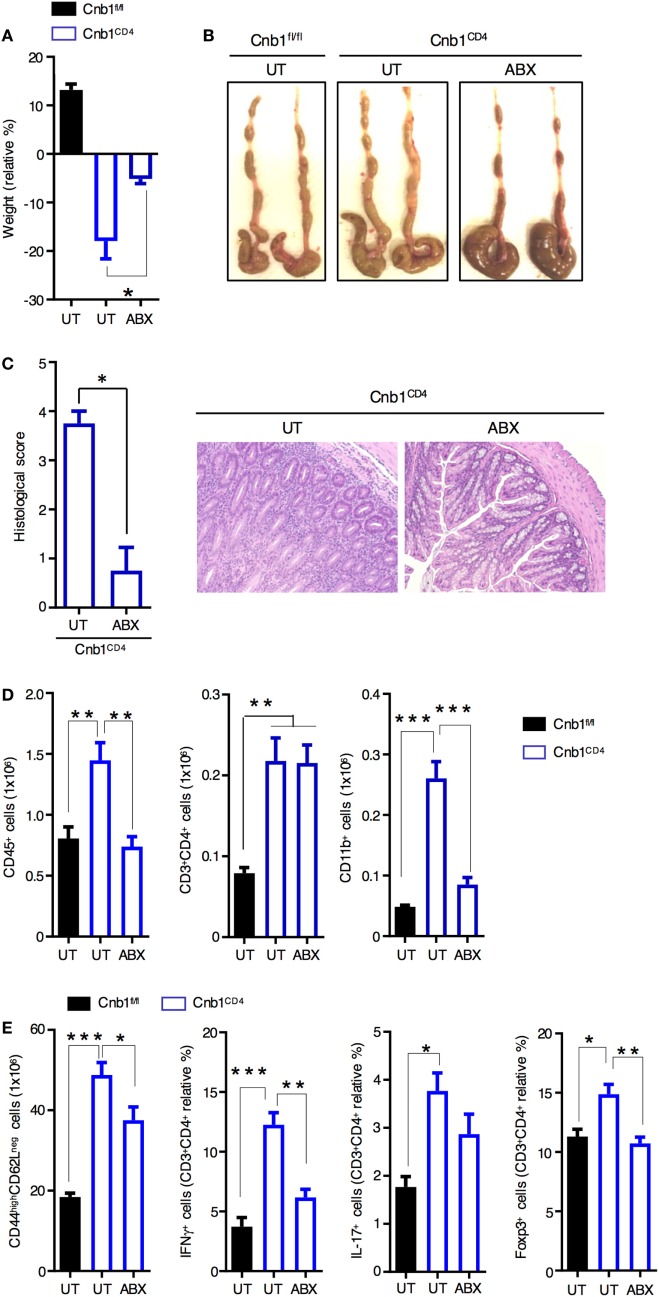
Figure 3.
Spontaneous intestinal inflammation is driven by the microbiota in Cnb1CD4 mice. (A) Change in body weight in untreated (UT) Cnb1fl/fl mice and Cnb1CD4 mice treated or not with antibiotics (ABX), from 4 weeks relative to baseline. (B) Macroscopic appearance of the colon in UT Cnb1fl/fl mice and Cnb1CD4 mice treated or not with ABX for 4 weeks. (C) Histological inflammation index of colon sections and representative hematoxylin and eosin staining (×10 magnification) of the colonic-lamina propria of ABX-treated Cnb1CD4 mice. (D) Absolute number of total leukocytes, CD4+ T cells, and CD11b+ cells infiltrating the colon of ABX-treated Cnb1CD4 mice. (E) Frequency of antigen-experienced CD44high CD4+ T cells secreting IFNγ or IL-17, or expressing the regulatory T-cell marker Foxp3+ obtained from Cnb1fl/fl UT mice and Cnb1CD4 mice treated or not with ABX for 4 weeks. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005 (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test). Data represent the means ± standard error of two independent experiments (n = 2–3 mice per group, per experiment).