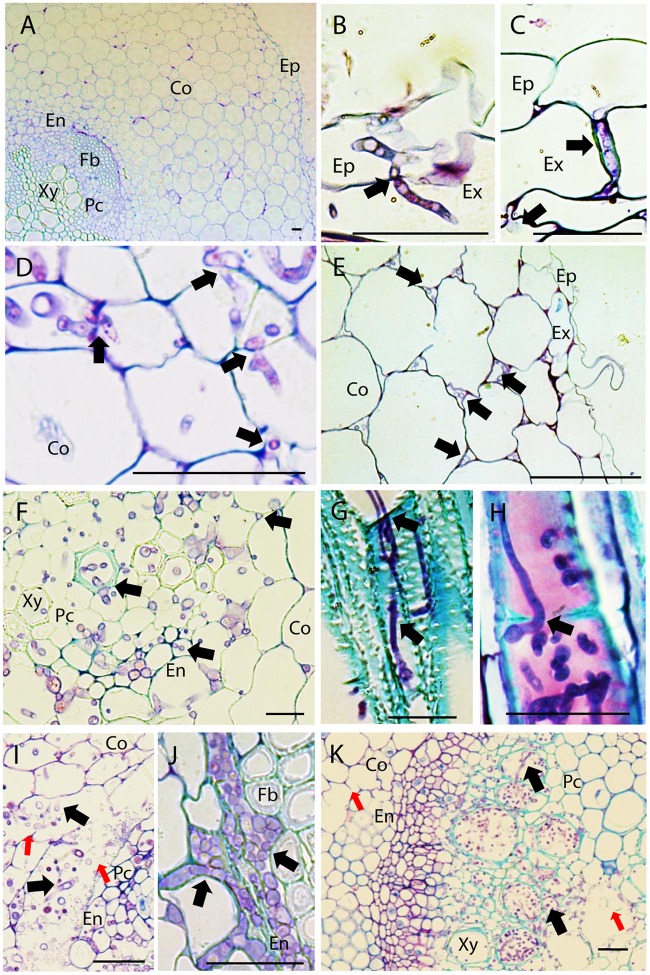
FIGURE 1.
Histopathology of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi (Fop) in pea accessions. The figure represents longitudinal and cross-sections of pea roots inoculated or not with Fop race 2 stained with TBO. (A) Cross-section of the susceptible P21 root maintained non-inoculated, showing a general view of pea root histology: epidermis, (Ep) cortex (Co), endodermis (En), parenchyma cells (Pc), Fiber cells (Fb), and xylem vessels (Xy). (B) Longitudinal section of Fop-inoculated root of the resistant accession P633 at 4 dpi, showing the penetration of an exodermal cell (Ex) by an infective hypha. Note the constriction of the hypha at site of cell wall penetration (black arrow). (C) Cross-section of the partially resistant accession Messire root at 7 dpi, showing the root penetration by Fop hypha growing between two exodermal cells (black arrow). (D) Cross-section of susceptible P629 roots at 7 dpi, showing intra- and intercellular progression of infective hyphae (Black arrows) through cortex and endodermis. Note the constriction of hypha at site of cortical cell penetration (Black arrows). (E) Cross section of Messire root at 7 dpi showing intercellular progression of infective hyphae through root cortex (Black arrows). (F) Cross-section of P21 root at 7 dpi after inoculation without root trimming showing abundant colonization of vascular tissue. (G) Longitudinal section of susceptible P21 root at 7 dpi showing inter- and intra-tracheary colonization of xylem vessels by elongation of infective hyphae (Black arrow). (H) Longitudinal section of resistant accession P633 at 7 dpi showing intra-tracheary colonization of xylem vessel by Fop conidia germinating through xylem perforation plate (Black arrow). (I) Cross section of the root of the susceptible accession P629 at 7 dpi showing intense degradation of endodermal cell layer (red arrows) and the abundant Fop development in the created intercellular space (Black arrows). (J) Cross-section of the partially resistant Messire root at 7 dpi showing abundant colonization of the intracellular space of endodermal cells by Fop (Black arrows). (K) Cross-section of the susceptible P21 hypocotyl showing abundant colonization of xylem vessels by Fop (Black arrows) and cell degradation in presence or absence of fungal structure (Red arrows). Bar = 25 μm.