FIG 2.
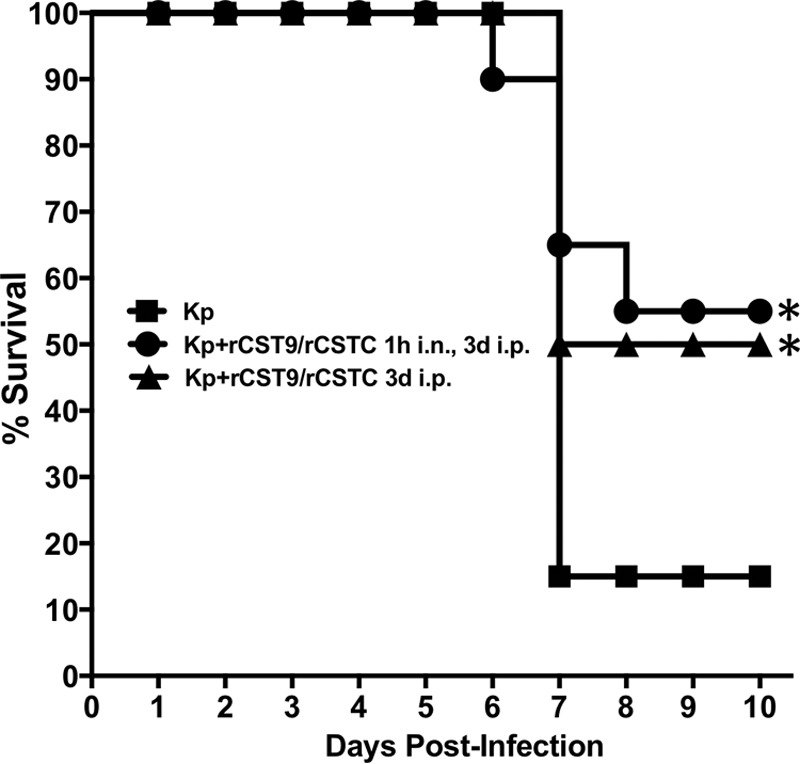
Optimal rCST9/rCSTC treatment regimens afforded protection against NDM-1 K. pneumoniae (Kp) pneumonia. BALB/c mice (n = 20 mice/group) were infected i.n. with NDM-1 K. pneumoniae (1.82 × 108 CFU/mouse) and then treated as follows: mice were given an i.n. dose of rCST9/rCSTC (50 pg of each/mouse) at 1 h p.i. followed by 500 pg (each) of rCST9/rCSTC per mouse at 3 days p.i., or mice were administered a single i.p. dose of rCST9/rCSTC (500 pg of each/mouse). Both rCST treatment regimens significantly increased survival compared to that of untreated NDM-1 K. pneumoniae-infected mice (P < 0.05). Data are presented as means ± SEM, and asterisks signify significant differences (P < 0.05).
