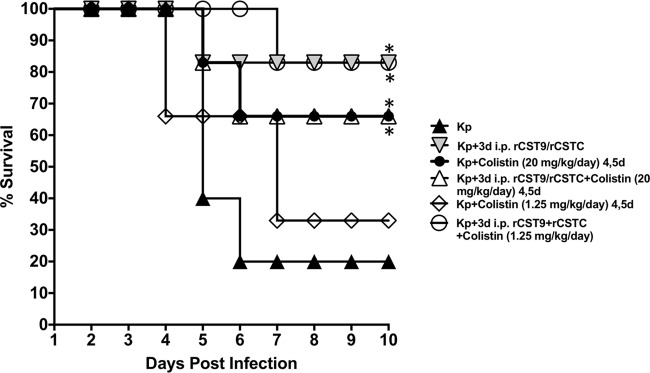
FIG 4.
rCST9/rCSTC and colistin polytreatment survival outcomes for mice infected with a lethal pulmonary challenge with NDM-1 K. pneumoniae. BALB/c mice (n = 15 mice/group) were infected i.n. with NDM-1 K. pneumoniae (1.82 × 108 CFU/mouse) and then given an i.p. dose of 500 pg (each) of rCST9/rCSTC per mouse at 3 days p.i. The mice were then given colistin (20 mg/kg/mouse or 1.25 mg/kg/day) i.p. 2 times/day (8 h apart) for 2 days, at 4 and 5 days p.i. rCST treatment followed by 20 mg/kg/day of colistin did not improve survival over that with rCST treatment alone. The high colistin dose alone or rCST treatment alone improved survival to a level equal to the survival rate of untreated infected mice (P < 0.05). Conversely, the polytreatments of rCSTs and a very low dose of colistin (1.2 mg/kg/day) did improve survival outcomes for infected mice compared to those with colistin treatment alone or those for untreated NDM-1 K. pneumoniae-infected mice (P < 0.05). Data are presented as means ± SEM, and asterisks signify significant differences (P < 0.05).