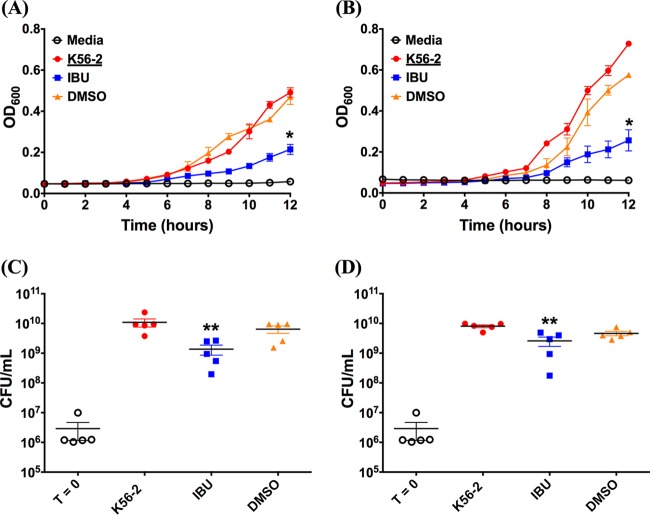
FIG 4.
Ibuprofen reduces the growth rate and the endpoint CFU counts of the Gram-negative bacterium B. cenocepacia K56-2 cultured in rich medium and artificial CF sputum (ASM). For both experiments, 1 × 106 CFU/ml of B. cenocepacia K56-2 was grown in duplicate wells of a 96-well plate at 37°C in MH broth and artificial CF sputum in the presence or absence of ibuprofen (IBU; 100 μg/ml) over a 12-h period. The OD600 was determined at 1-h intervals to compare the growth rates for B. cenocepacia K56-2 in MH broth (A) and artificial CF sputum (B). At 12 h, the bacteria were diluted and plated to determine the bacterial burden (the number of CFU per milliliter), as shown, in MH broth (C) and artificial CF sputum (D). Controls included uninoculated growth medium (not shown), growth medium with bacteria alone, and growth medium containing DMSO (5%, vol/vol) without ibuprofen (0 μg/ml) inoculated with bacteria. Each data set represents the mean from 5 independent experiments (total, 10 replicates per treatment), and the data are presented as the mean ± standard error. Symbols in panels C and D: empty circles, starting inoculum of bacteria; filled circles, bacteria alone; filled squares, bacteria treated with ibuprofen; filled upright triangles, bacteria in growth medium containing DMSO but no ibuprofen. A paired t test was used to analyze the differences in the endpoint OD600 for growth curves, and a two-tailed, nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to analyze the differences in CFU counts. *, P < 0.05 compared to the control; **, P < 0.01 compared to the control.