FIG 6.
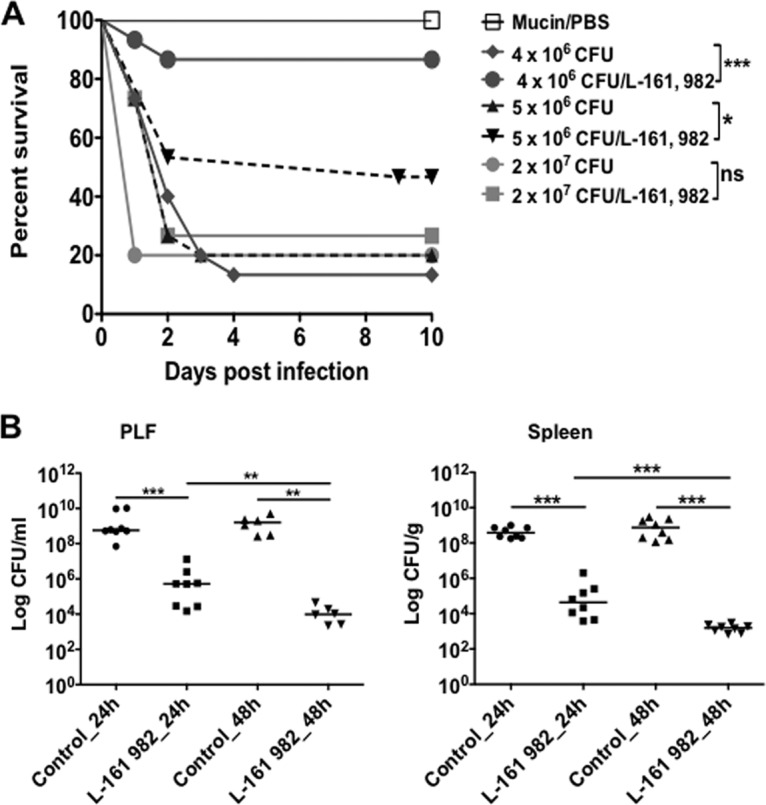
Effect of L-161,982 on survival and microbial burden. Mice were infected intraperitoneally with 0.2 ml of the indicated inoculum of S. aureus NRS383 in 3% hog gastric mucin–PBS. One group of mice per inoculum received either the vehicle or L-161,982 at a dose of 10 mg/kg by i.p. injection, as indicated in Materials and Methods. (A) Mortality was assessed using the Kaplan-Meier test and was compared to that of the control groups (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ns, not significant; n = 15/group). (B) The microbial burden in peritoneal lavage fluid (PLF) and spleen between the untreated (control) and treated (L-161,982) groups was assessed at 24 and 48 h postinoculation (n = 6 to 8/group). Values are plotted as the median number of CFU and were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). Data shown are representative of those from three replicate experiments.
